Support for OpenShift Operators
Learn about the backup and restore of OpenShift operators with Trilio for Kubernetes.
Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM) helps users install, update, and manage the lifecycle of Kubernetes native applications (Operators) and their associated services running across their OpenShift Container Platform clusters. The OpenShift Container Platform web console provides management screens for cluster administrators to install Operators and grant specific projects access to the catalog of Operators available on the cluster.
Please review the official documentation for more information about OLM operators and their concepts.
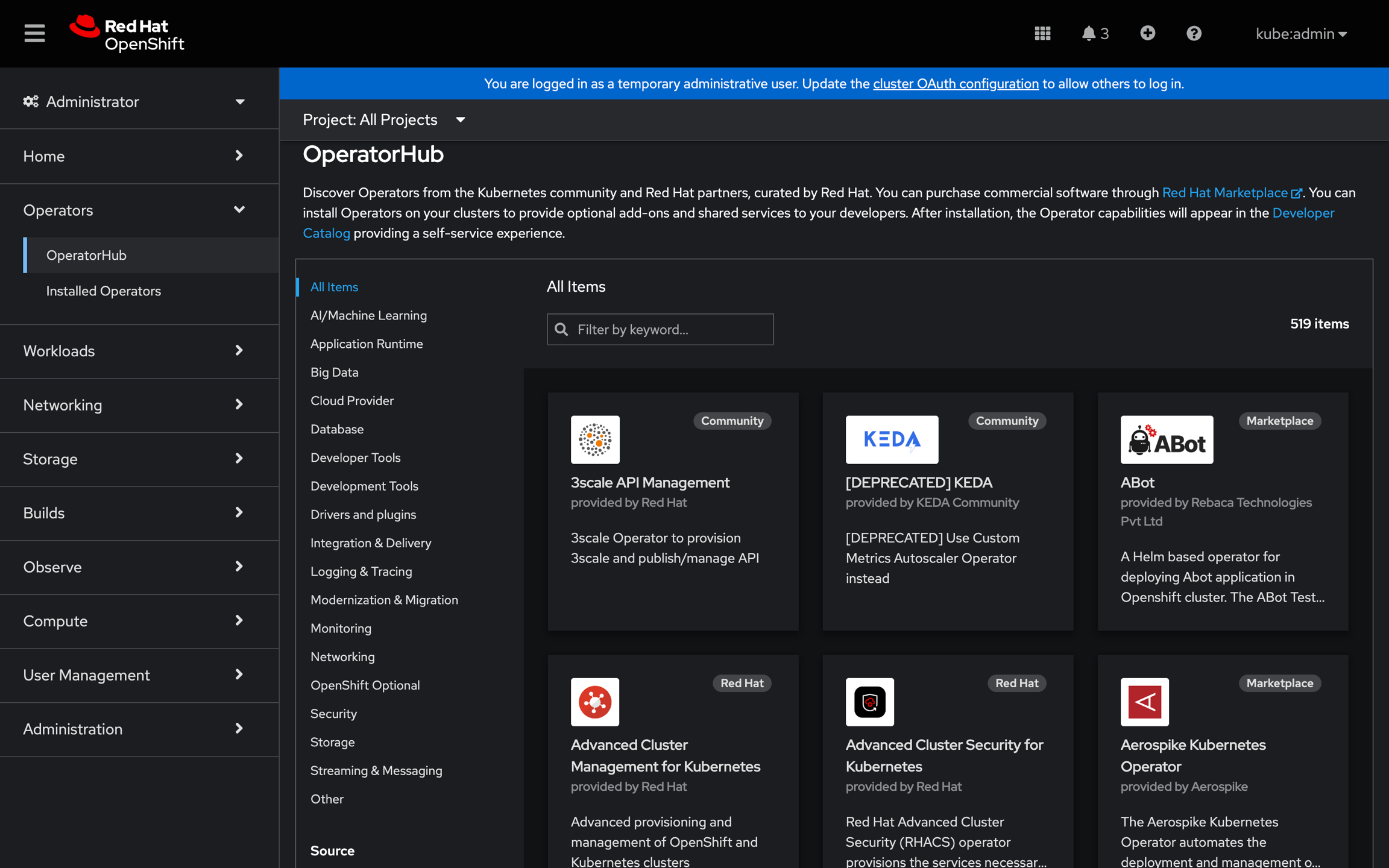
Cloud Native Backup and Restore of OpenShift Operators
OLM efficiently installs and upgrades cloud-native applications on the OpenShift cluster via its web console, and the OpenShift UI provides visibility into your deployed applications.
Traditional methods, such as namespace-based backup, fall short in recognizing OLM operators. The namespace approach may miss certain operators and their associated custom resources if they exist in a different namespace. Consequently, a restore done using this method might be incomplete, and the restored applications may not appear as they did before the backup.
Trilio, on the other hand, excels at restoring OpenShift operators seamlessly. Recovering directly from your backup target, Trilio replaces the application in a way that maintains its continuous life cycle, as if no interruption occurred. Trilio ensures the preservation of OLM operators in their original forms, allowing them to be viewed seamlessly on the OpenShift UI. These operators can seamlessly resume their life cycles, receiving upgrades and updates akin to operators installed from the operator hub.
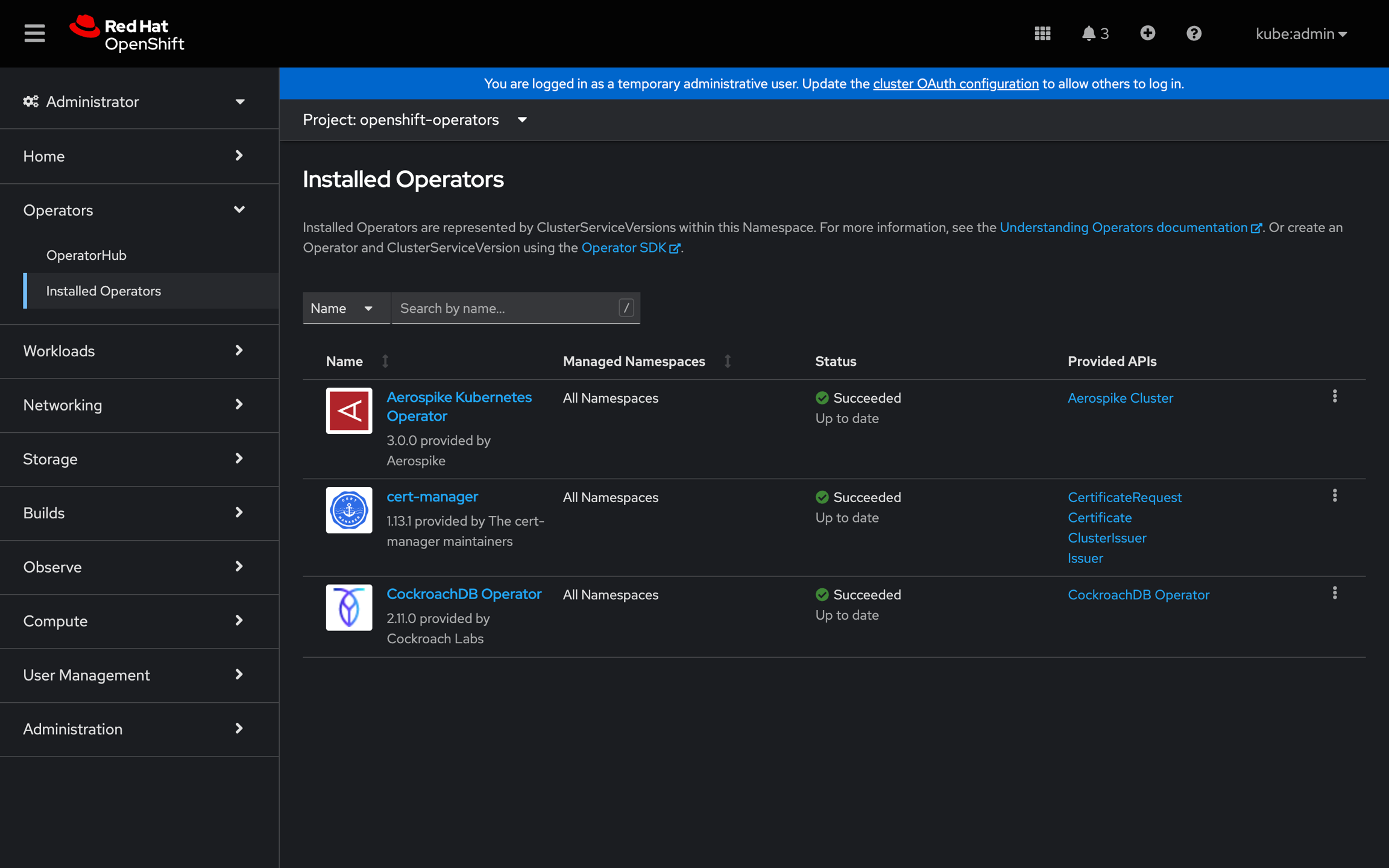
Best Practice for OLM Dependencies
OLM operators may rely on other OLM operators designated as dependent operators. When installing an operator with dependencies, the associated dependent operators are automatically included. For detailed insights into OLM dependency resolution, refer to the official documentation.
Trilio adeptly recognizes all dependent operators linked to any operator and ensures their inclusion in the backup, along with their respective custom resources.
During the restoration process, Trilio follows a reverse sequence, starting with the restoration of dependent operators and their custom resources before moving on to the parent operator for which the backup was initiated.
In cases where a particular operator is already present in the cluster, Trilio detects this presence, skips those operators, and focuses on restoring their custom resources, which seamlessly align with the existing operators.
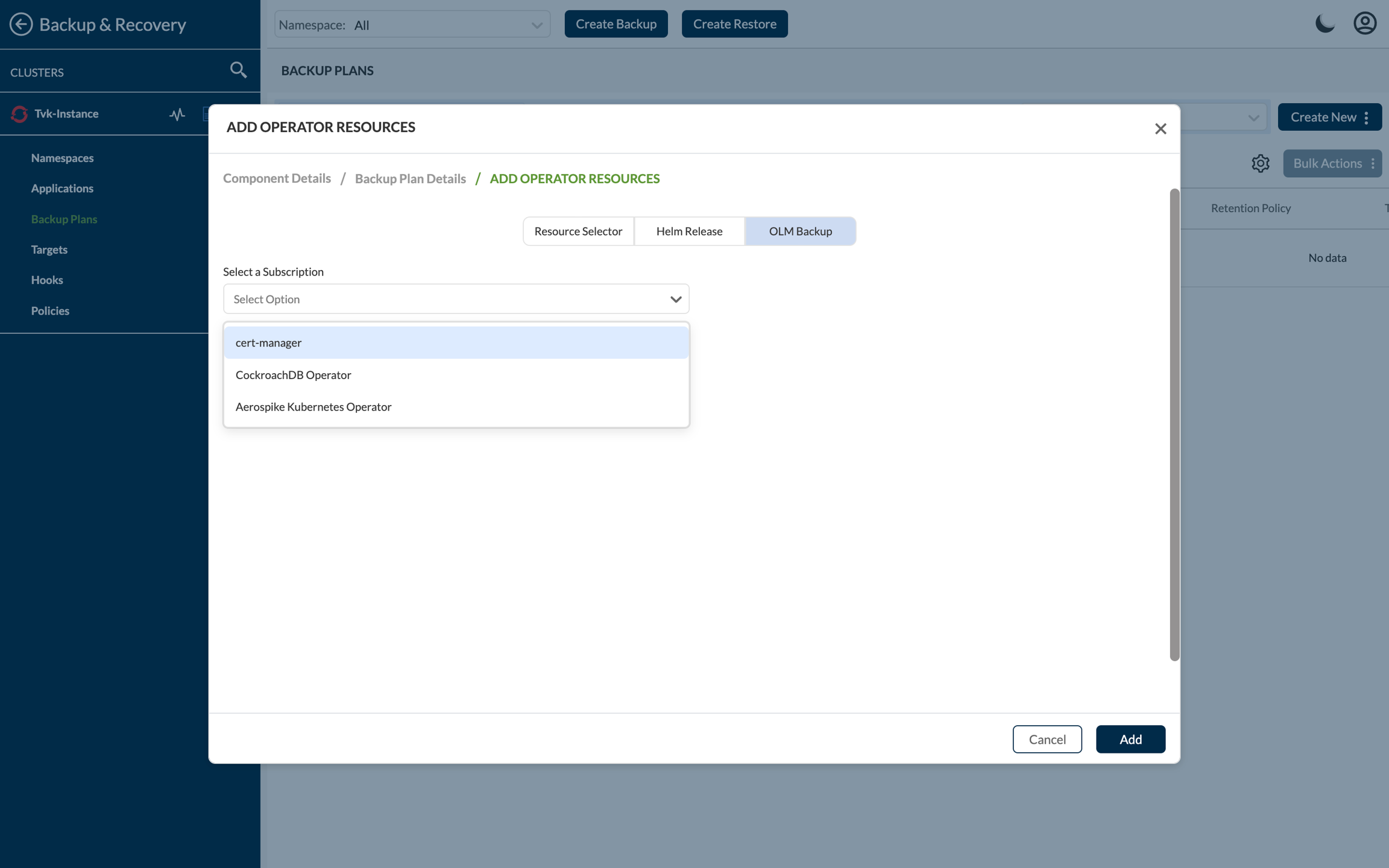
Backup Plan for OLM operator
To create a backup for an OLM operator, generate a Backup Plan at the application level and pick the operator along with its custom resources. In the Backup Plan's operator section, locate the OLM operators segment. By selecting this, you'll access a list of OLM operators present in the cluster, enabling you to choose the specific operator for backup.
After choosing the operator, it will display both the custom resources associated with it and any dependent operators it installs. Now, pick the custom resources you wish to incorporate into your backup. A sample Backup Plan will appear like this:
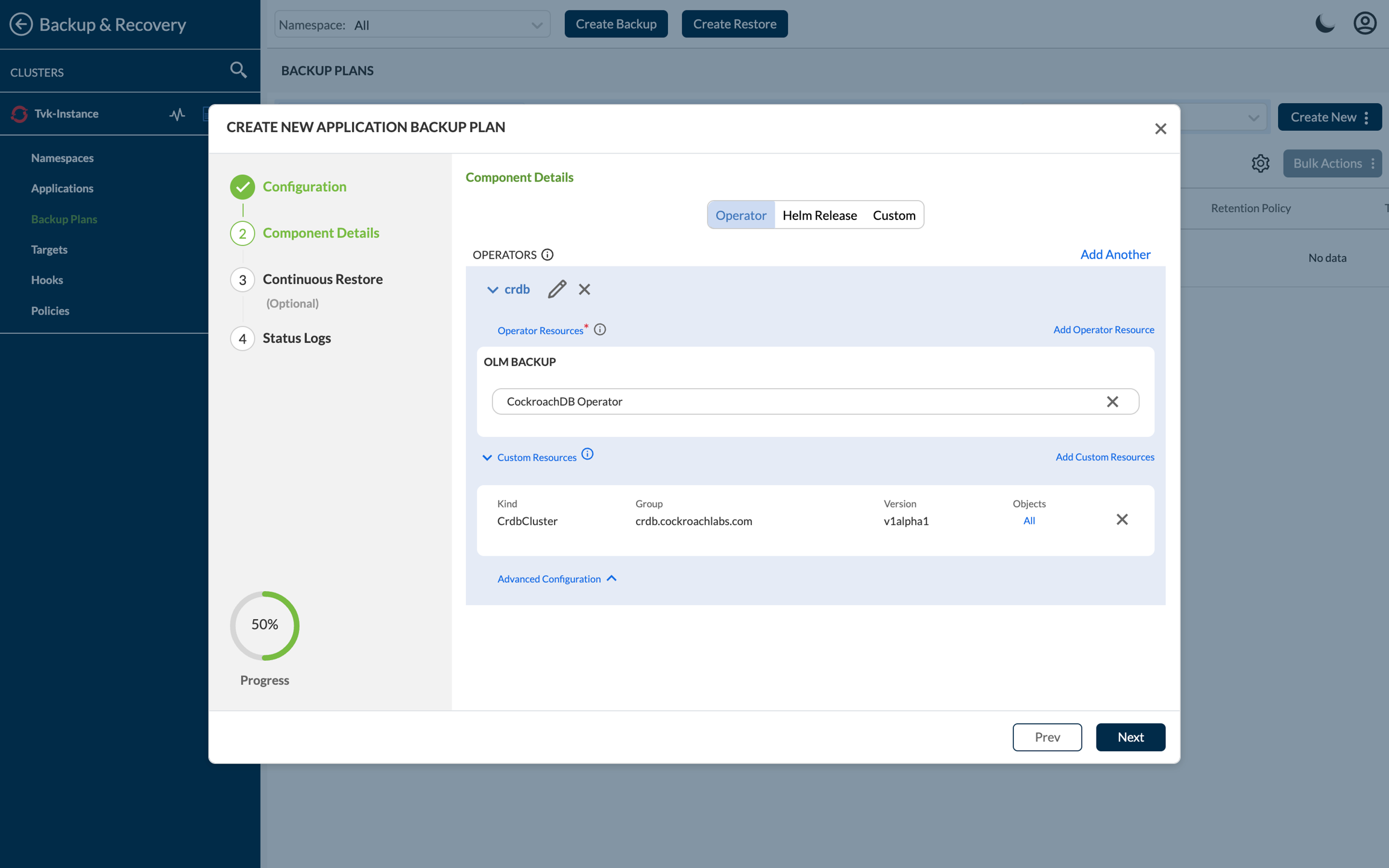
Click on Next and create the backupplan, which backups the OLM operators in its native form.
Note: Namespace backup doesn't support the OLM backups in its native form, so to backup OLM operators user has to define application level backupplan.