Getting Started with Trilio on Red Hat OpenShift (OCP)
Learn to install, license, test, and monitor Trilio for OpenShift
Table of Contents
What is Trilio for OpenShift?
Trilio for OpenShift is a cloud-native backup and restore application. Being a cloud-native application for Kubernetes, all operations are managed with CRDs (Customer Resource Definitions).
Trilio utilizes Control Plane and Data Plane controllers to carry out the backup and restore operations defined by the associated CRDs. When a CRD is created or modified the controller reconciles the definitions to the cluster.
Trilio gives you the power and flexibility to backup your entire cluster or select a specific namespace(s), label, Helm chart, or Operator as the scope for your backup operations.
In this tutorial, we'll show you how to install and test operation of Trilio for OpenShift on your Red Hat OpenShift cluster.
Prerequisites
Before installing Trilio for OpenShift, please review the compatibility matrix to ensure Trilio can function smoothly in your Kubernetes environment.
Trilio for OpenShift requires a compatible Container Storage Interface (CSI) driver that provides the Snapshot feature.
Check the Kubernetes CSI Developer Documentation to select a driver appropriate for your backend storage solution. See the selected CSI driver's documentation for details on the installation of the driver in your cluster.
Trilio will assume that the selected storage driver is a supported CSI driver when the volumesnapshotclass and storageclassare utilized.
About the vSphere CSI Driver and Trilio for OpenShift
Starting with OpenShift 4.11 it is possible to use the vSphere CSI Driver with Trilio for OpenShift, however the components which support the required CSI Snapshot functionality must be added by deploying the vSphere CSI Snapshot Components.
Visit the vSphere CSI Driver repository and follow the steps provided there to enable and install the CSI driver Snapshot Components on your OpenShift cluster.
There is a special consideration for installing the vSphere Snapshot Components on OpenShift:
MacOS example:
sed -i '' -e 's/vmware-system-csi/openshift-cluster-csi-drivers/g' -e 's/vsphere-csi-controller/vmware-vsphere-csi-driver-controller/g' deploy-csi-snapshot-components.sh
GNU example:
sed -i 's/vmware-system-csi/openshift-cluster-csi-drivers/g; s/vsphere-csi-controller/vmware-vsphere-csi-driver-controller/g' deploy-csi-snapshot-components.sh
Trilio for OpenShift requires the following Custom Resource Definitions (CRD) to be installed on your cluster:VolumeSnapshot, VolumeSnapshotContent, and VolumeSnapshotClass.
Installing the Required VolumeSnapshot CRDs
Before attempting to install the VolumeSnapshot CRDs, it is important to confirm that the CRDs are not already present on the system.
To do this, run the following command:
If CRDs are already present, the output should be similar to the output displayed below. The second column displays the version of the CRD installed (v1 in this case). Ensure that it is the correct version required by the CSI driver being used.
Installing CRDs
Be sure to only install v1 version of VolumeSnapshot CRDs
Read the external-snapshotter GitHub project documentation. This is compatible with v1.22+.
Run the following commands to install directly, check the repo for the latest version:
For non-air-gapped environments, the following URLs must be accessed from your Kubernetes cluster.
Access to the S3 endpoint if the backup target happens to be S3
Access to application artifacts registry for image backup/restore
If the Kubernetes cluster's control plane and worker nodes are separated by a firewall, then the firewall must allow traffic on the following port(s)
9443
Verify Prerequisites with the Trilio Preflight Check
Make sure your cluster is ready to Install Trilio by installing the Preflight Tool and running the Trilio Preflight Check.
Trilio provides a preflight check tool that allows customers to validate their environment for Trilio installation.
The tool generates a report detailing all the requirements and whether they are met.
Fix any missing requirements before proceeding with Trilio installation.
Upgrading from a Version Older Than 3.0.0?
Inline or rolling upgrades from Trilio versions older than 3.0.0 are not supported in Red Hat OpenShift.
If running an older version of Trilio, go to the Installed operator page and uninstall the existing Trilio for OpenShift operator.
Proceed with the installation steps outlined in this document.
Be sure you install the Trilio operator that bears the Certified logo.
Installing older versions by adding a Custom CatalogSource (Optional)
Follow the steps below to Install Trilio via a Custom CatalogSource.
The example YAML below would install the CatalogSource for version 3.0.2 as configured on the image spec line.
Validate the catalogsource was successfully installed by running the following command
oc get catalogSource k8s-triliovault-manifest -n openshift-marketplace
Navigate to the OperatorHub console and verify that the Trilio operator is now available to be installed. Log out and back in again if you do not see the operator.
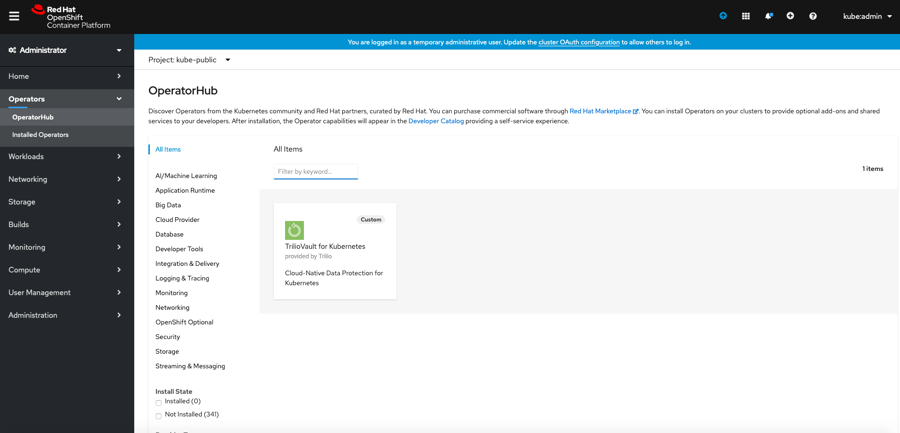
Proceed with the installation of Trilio for OpenShift as described in the Installing Trilio for Kubernetes on Red Hat OpenShift Tutorial.
Follow the offical documentation for adding a CatalogSource in restricted environments:
For OCP 4.6 - follow these instructions
For OCP 4.8 - follow these instructions
For OCP 4.10 - follow these instructions
Install Trilio for OpenShift
Trilio is available as a Certified Operator in the embedded OperatorHub for OpenShift environments.
Log in to the RedHat OpenShift Container Platform.
From the Operators dropdown in the left panel menu, select OperatorHub.
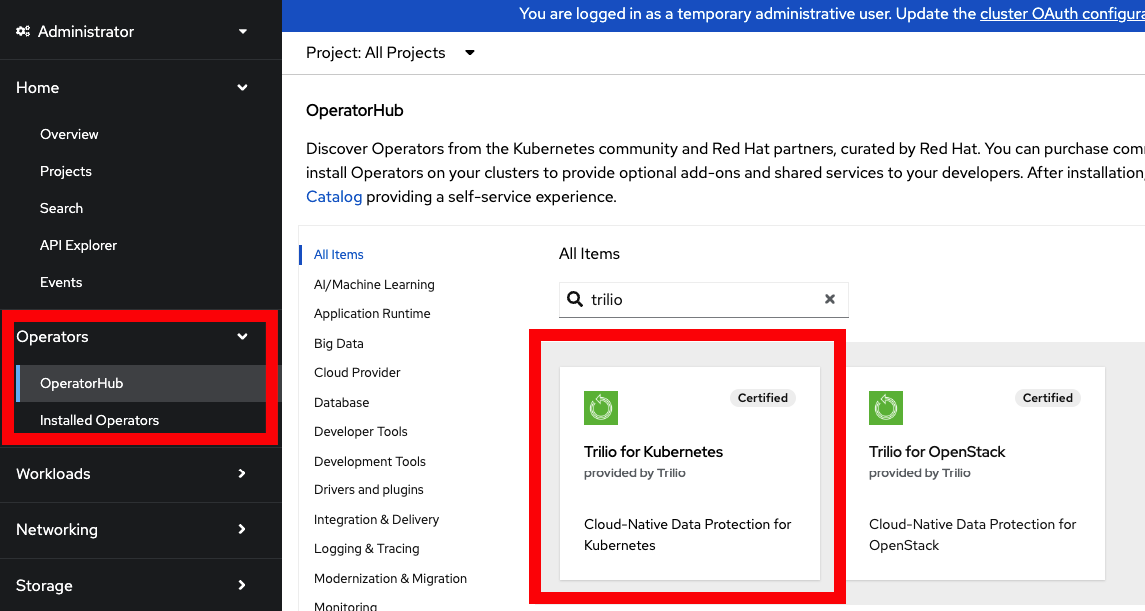
In the search field, start to type the word 'Trilio.' The search narrows as you type. Alternatively, filter by a category, and you will find "Trilio for Kubernetes" in the Database, Monitoring, Security, and Developer Tools categories.
Select the result for "Trilio for Kubernetes" that bears the Certified approval logo.
Click Install

The Trilio for OpenShift operator will automatically create a trilio-system namespace as the default. You can optionally install it in the openshift-operators namespace. From the Install Operator page, beneath Update Approval, you can choose between Automatic or Manual. Also, you can enable the Trilio's Console Plugin, and you will have a Trilio Backups section in the OpenShift Console
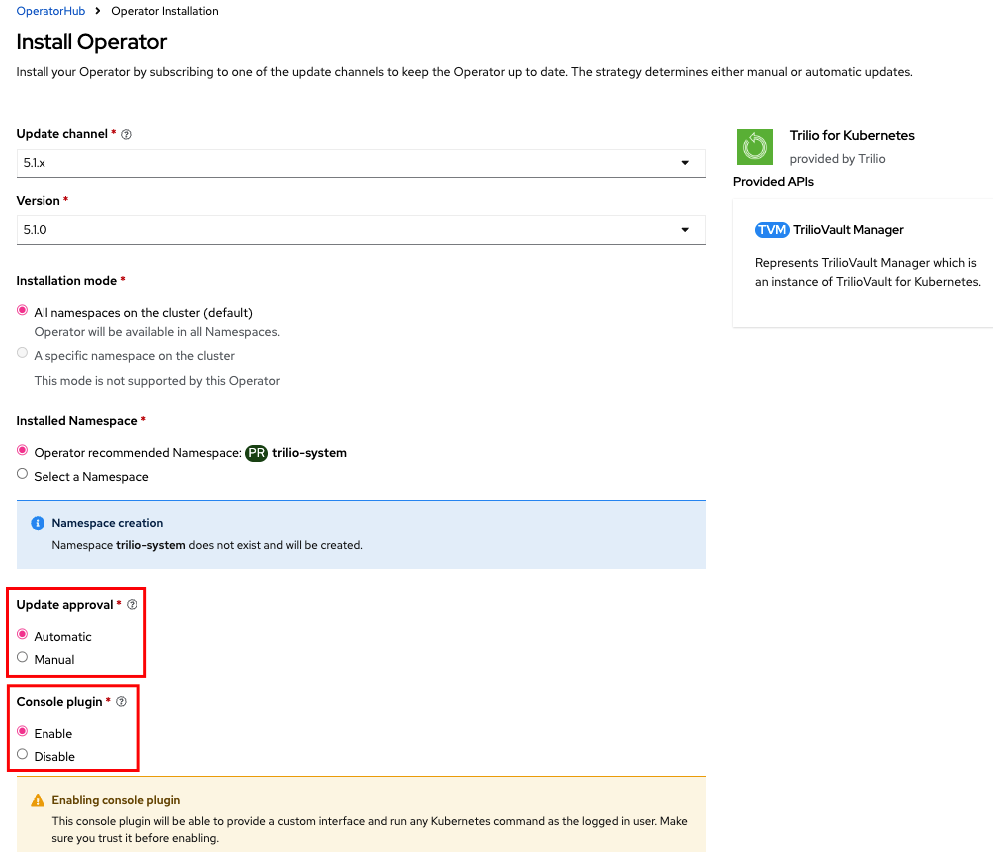
Click Install
After installation, ensure that the notification indicates success.
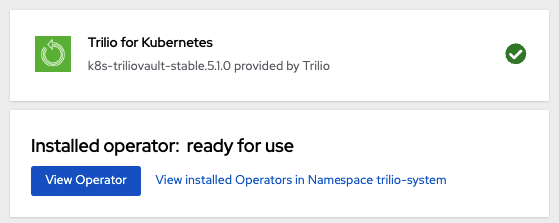
If you enabled the console plugin, you will get a message to refresh the console
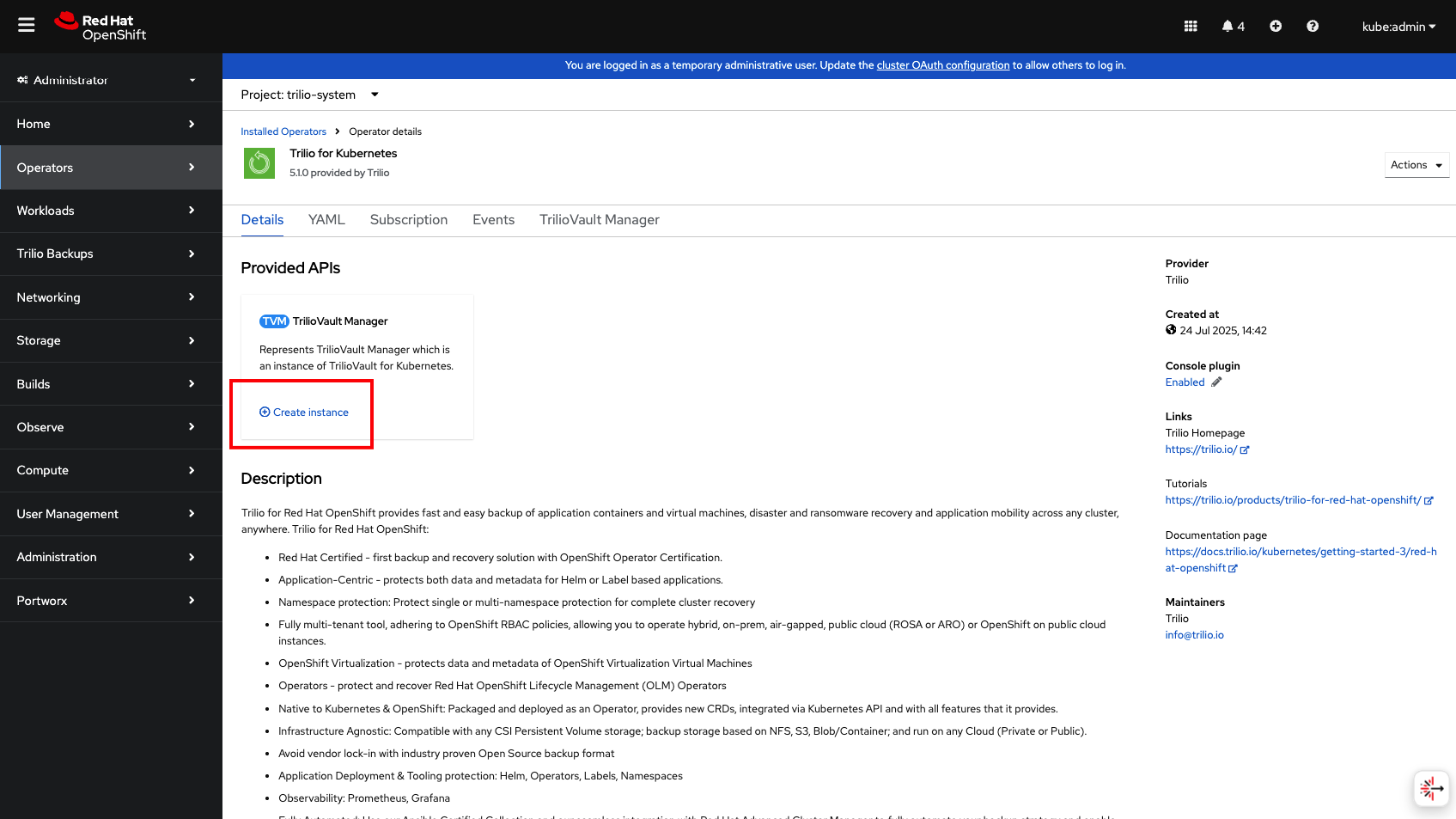
Once the installation completes successfully, click on View Operator. Click on Create instance
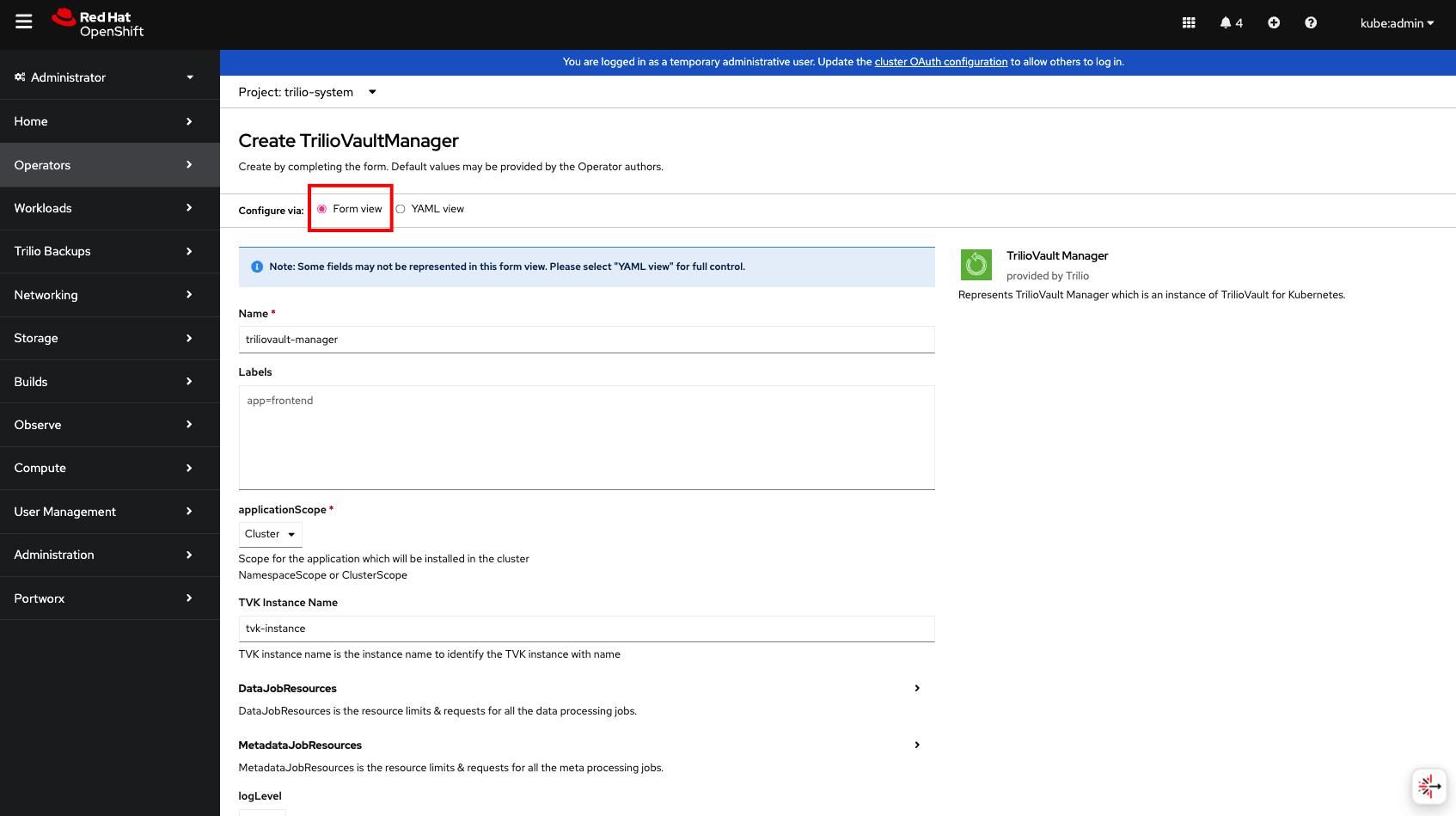
Fill out the required fields in "form view" to create the Trilio Manager CR. Recommended values to configure the Trilio Manager are pre-populated; you can alter the input based on your requirement. Click on Create to continue.
Check out Modifying Default T4K Configuration for explore more tvk configuration.
Once completed the Trilio Manager will be deployed.
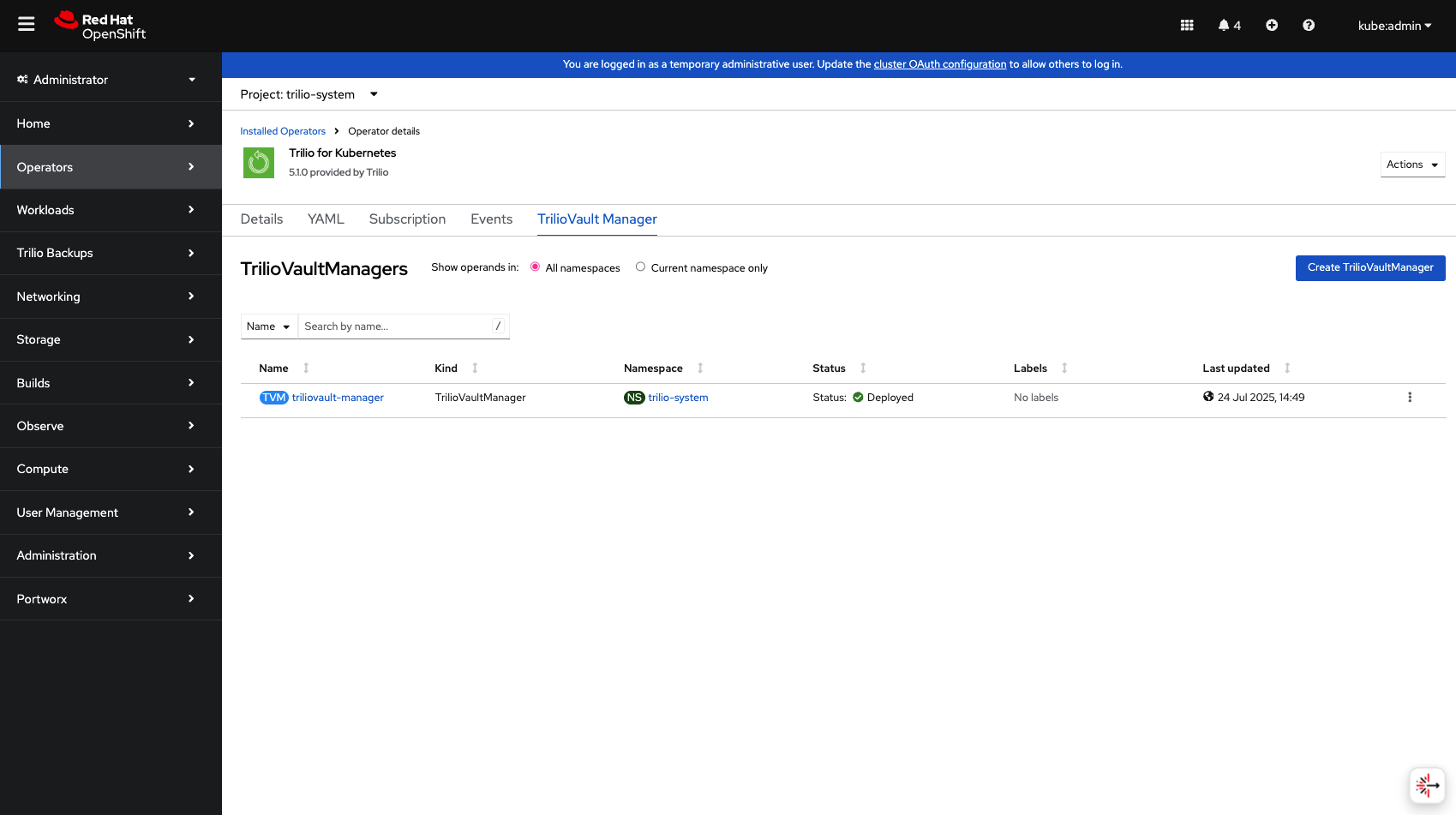
Click on the triliovault-manager custom resource link. Take note of the dashboard link, this is the link to the Trilio Management Console UI.
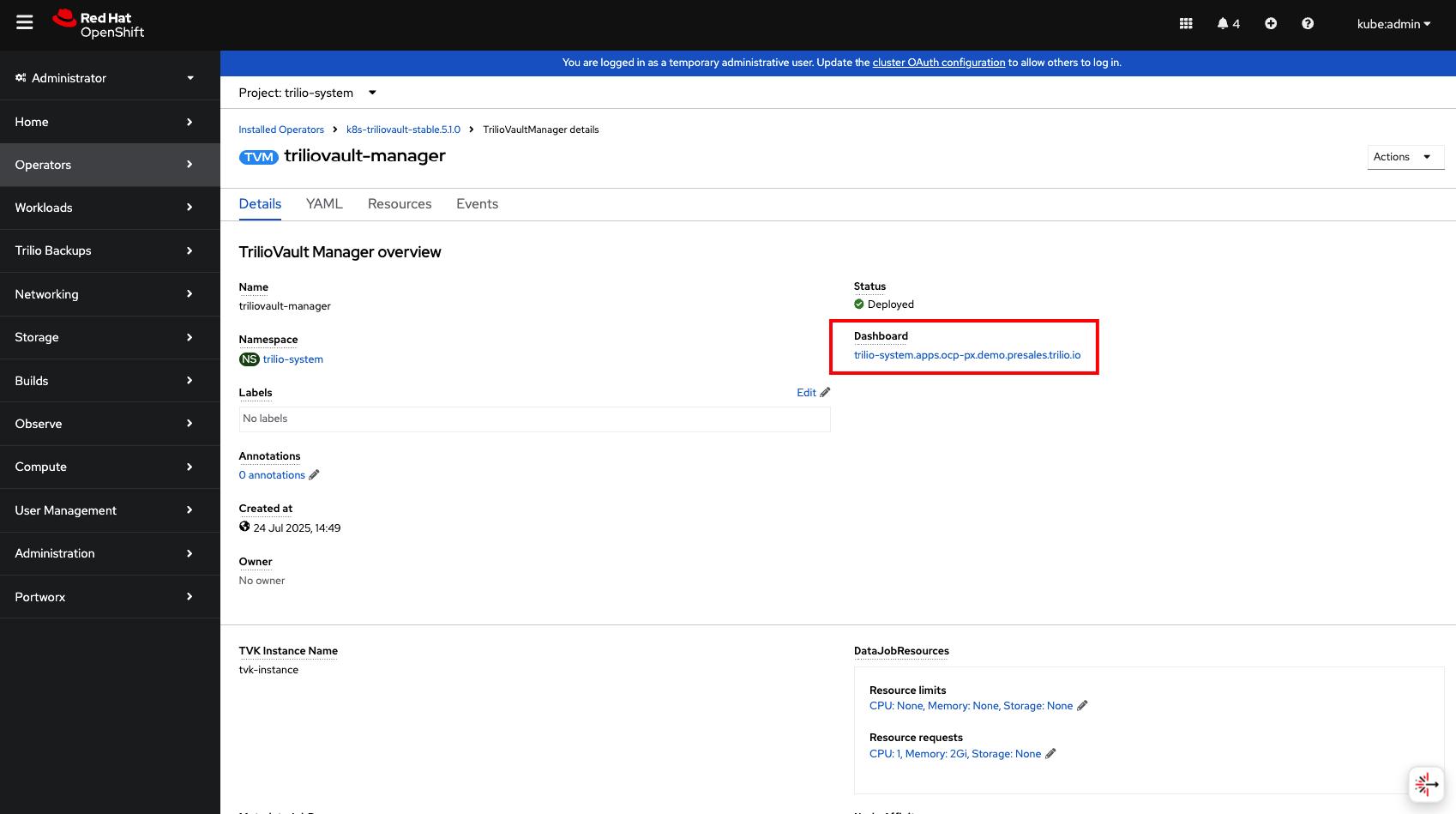
Check the resources section and make sure all resources are in a running state.
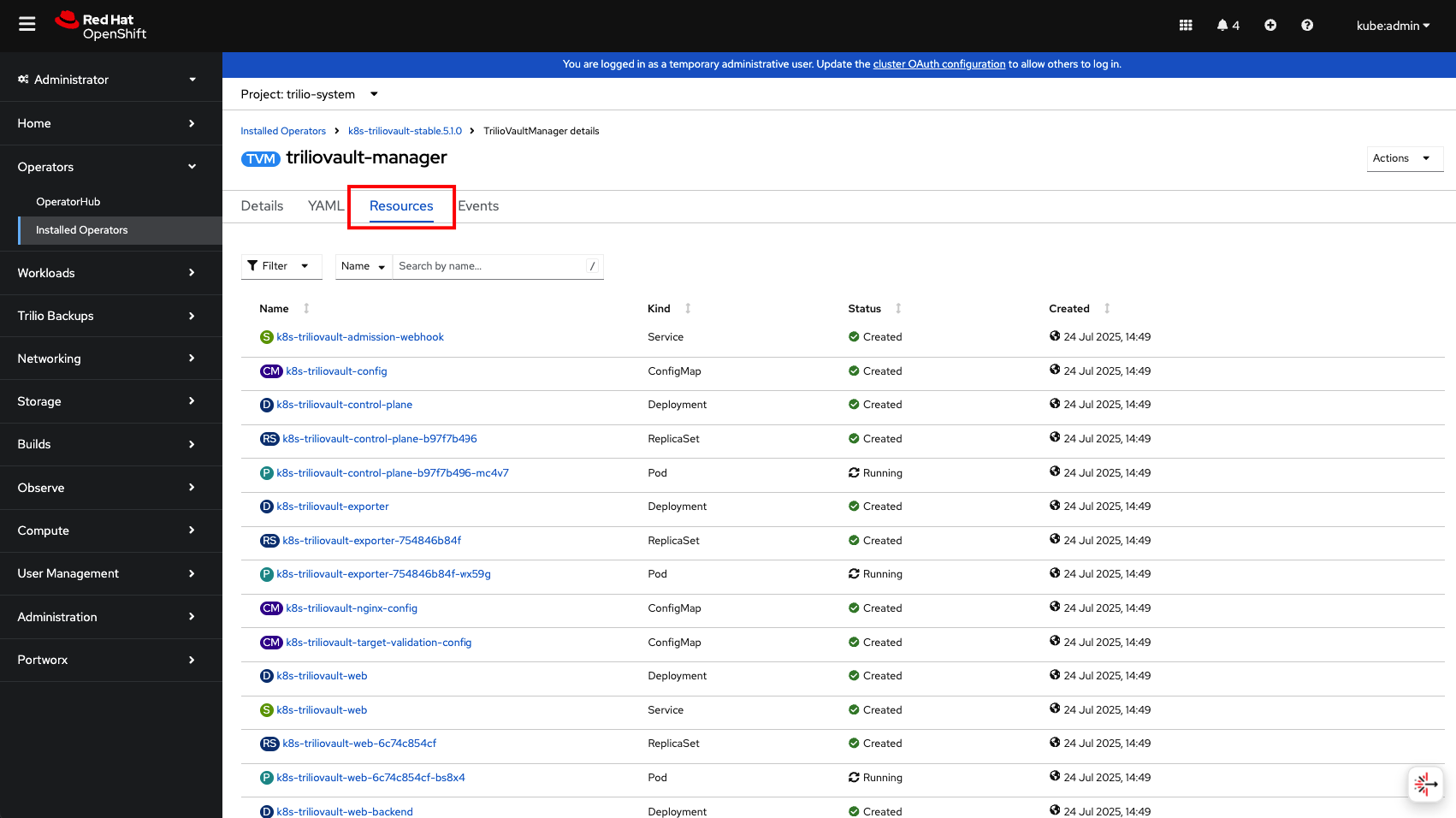
Now click on the dashboard link to access the Management Console UI:

If the Trilio Management Console UI is not accessible, you may optionally, for a default ingress scenario, run the following command to ensure that Trilio can use the built-in ingress controller for OpenShift within the cluster for networking. Try accessing the UI again after running this command.
A Note About Proxy-enabled Environments
Trilio for OpenShift automatically picks up the proxy settings defined for the OpenShift cluster in the proxy/cluster CR. No user configuration is required in this case.
For more details on how to configure the cluster-wide proxy in OpenShift, refer to the official documentation.
Sign-in to the Trilio Management Console
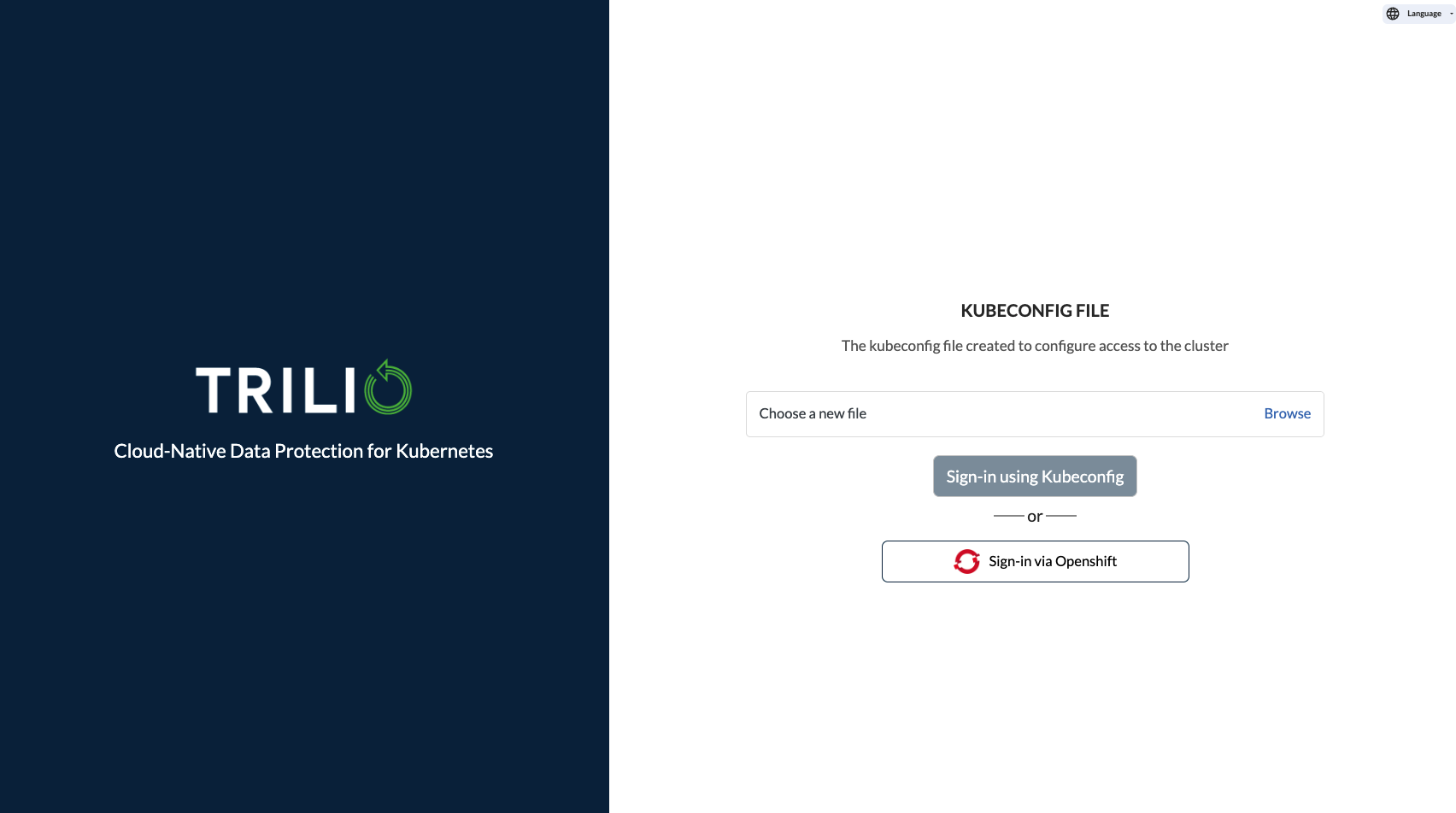
You can sign-in to the Trilio Management Console in your browser (Step 14) by authenticating with a valid kubeconfig file or with your OpenShift credentials.
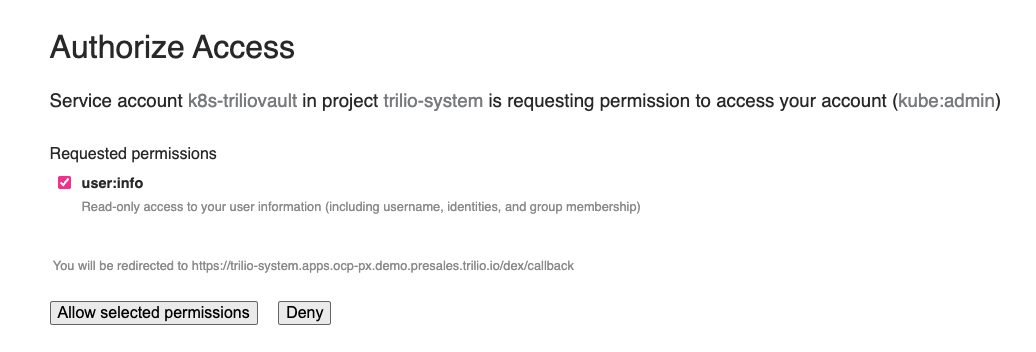
Permission Authorization
When you login for the first time, you will have to authorize this
End User License Agreement
The nest screen is acceptance of the End User License Agreement.
After accepting you will see the Trilio UI
If You are using a kubeconfig file for authentication:
use the Browse field to search and select your file.
Then press the Sign-in using kubeconfig/credentials button.
Alternatively, to use OpenShift authentication credentials:
Press the Sign-in via OpenShift button.
On the login screen, select the OpenShift account that you wish to sign in with.
If you are not already logged in to your OpenShift account, you will be prompted to sign in with your OpenShift username and password.
Licensing Trilio for OpenShift
Although a cluster license enables Trilio features across all namespaces in a cluster, the license only needs to be applied in the namespace where Trilio is installed. For example, trilio-system namespace.
1. Obtain a license by getting in touch with us here. The license file will contain the license key.
2. Apply the license file to a Trilio instance using the command line or UI:
Execute the following command:
2. If the previous step is successful, check that the output generated is similar to the following:
Additional license details can be obtained using the following: oc get license -o json -m trilio-system
Prerequisites:
Authenticate access to the Management Console (UI). Refer to .
Configure access to the Management Console (UI). Refer to Configuring the UI.
If you have already executed the above prerequisites, then refer to the guide for applying a license in the UI: Actions: License Update
Upgrading a license
A license upgrade is required when moving from one license type to another (Free/Basic -> Enterprise and vice-versa).
Trilio maintains only one instance of a license for every installation of Trilio for OpenShift.
To upgrade a license, run kubectl apply -f <licensefile> -n <install-namespace> against a new license file to activate it. The previous license will be replaced automatically.
Create a Target
The Target CR (Customer Resource) is defined from the Trilio Management Console or from your own self-prepared YAML.
The Target object references the NFS or S3 storage share you provide as a target for your backups/snapshots. Trilio will create a validation pod in the namespace where Trilio is installed and attempt to validate the NFS or S3 settings you have defined in the Target CR.
Trilio makes it easy to automatically create your Target CR from the Management Console.
Learn how to Create a Target from the Management Console
Take control of Trilio and define your own self-prepared YAML and apply it to the cluster using the oc/kubectl tool.
Example S3 Target
See more Example Target YAML
Testing Backup, Snapshot and Restore Operation
Trilio is a cloud-native application for Kubernetes, therefore all operations are managed with CRDs (Custom Resource Definitions). We will discuss the purpose of each Trilio CRs and provide examples of how to create these objects Automatically in the Trilio Management Console or from the oc/kubectl tool.
About Backup Plans
The Backup Plan CR is defined from the Trilio Management Console or from your own self-prepared YAML.
The Backup Plan CR must reference the following:
Your Application Data (label/helm/operator)
BackupConfig
Target CR
Scheduling Policy CR
Retention Policy CR
SnapshotConfig
Target CR
Scheduling Policy CR
Retention Policy CR
A Target CR is defined from the Trilio Management Console or from your own self-prepared YAML. Trilio will test the backup target to insure it is reachable and writable. Look at Trilio validation pod logs to troubleshoot any backup target creation issues.
Retention and Schedule Policy CRs are defined from the Trilio Management Console or from your own self-prepared YAML.
Scheduling Policies allow users to automate the backup/Snapshot of Kubernetes applications on a periodic basis. With this feature, users can create a scheduling policy that includes multiple cron strings to specify the frequency of backups.
Retention Policies make it easy for users to define the number of backups/snapshots they want to retain and the rate at which old backups/snapshots should be deleted. With the retention policy CR, users can use a simple YAML specification to define the number of backups/snapshots to retain in terms of days, weeks, months, years, or the latest backup/snapshots. This provides a flexible and customizable way to manage your backup/snapshots retention policy and ensure you meet your compliance requirements.
The Backup and Snapshot CR is defined from the Trilio Management Console or from your own self-prepared YAML.
The backup/snapshot object references the actual backup Trilio creates on the Target. The backup is taken as either a Full or Incremental backup as defined by the user in the Backup CR. The snapshpt is taken as Full snapshot only.
Creating a Backup Plan
Trilio makes it easy to automatically create your backup plans and all required target and policy CRDs from the Management Console.
Take control of Trilio, define your self-prepared YAML, and apply it to the cluster using the oc/kubectl tool.
Example Namespace Scope BackupPlan:
Target in the backupConfig and snapshotConfig needs to be the same. User can specify different retention and schedule policies under backupConfig and snapshotConfig.
See more Examples of Backup Plan YAML
Creating a Backup
Learn more about Creating Backups from the Management Console
Creating a Snapshot
Learn more about Creating Snapshots from the Management Console
About Restore
A Restore CR (Custom Resource) is defined from the Trilio Management Console or from your own self-prepared YAML. The Restore CR references a backup object which has been created previously from a Backup CR.
In a Migration scenario, the location of the backup/snapshot should be specified within the desired target as there will be no Backup/Snapshot CR defining the location. if you are migrating Snapshot then make sure that then then actual Persistent Volume snapshots are accessible from the other cluster.
Trilio restores the backup/snapshot into a specified namespace and upon completion of the restore operation, the application is ready to be used on the cluster.
Creating a Restore
Trilio makes it easy to automatically create your Restore CRDs from the Management Console.
Learn more about Creating Restores from the Management Console
Take control of Trilio, define your self-prepared YAML, and apply it to the cluster using the oc/kubectl tool.
See more Examples of Restore YAML
Observability into Trilio for OpenShift
The Trilo Metrics Exporter provides Trilio performance data in the Prometheus format and makes it consumable as a target for your existing Prometheus based monitoring stack.
OpenShift ships with a native monitoring stack based on Prometheus which can be configured to pull in Trilio metrics.
The native Prometheus deployment can be accessed from the prometheus-k8s route in the openshift-monitoring namespace.
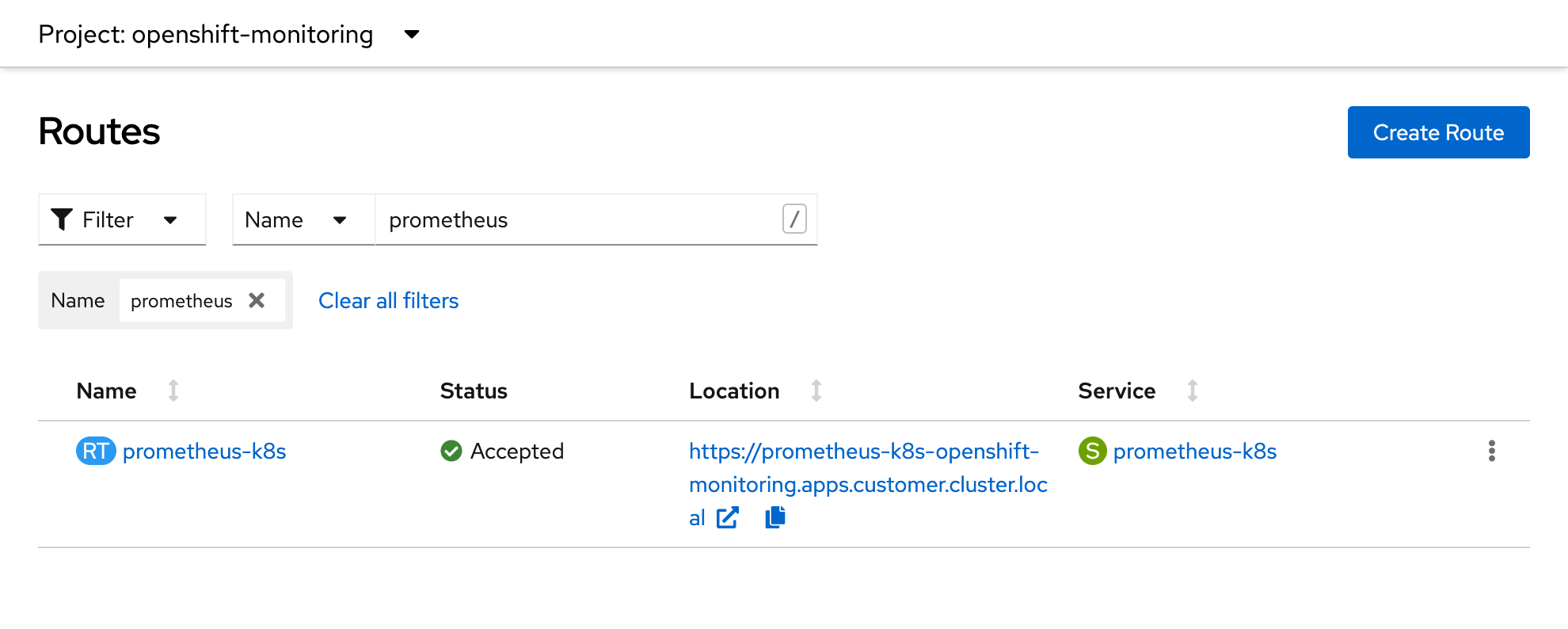
The Trilio Exporter is installed and running in the same namespace in which you have installed Trilio however, there will still be a need to create a namespace label, service, service monitor, and cluster role binding to allow the OpenShift native Prometheus pod to consume these metrics.
We will discuss the steps required to pull Trilio metrics into the native OpenShift monitoring stack.
Consuming Trilio Metrics on OpenShift's Native Prometheus Deployment
The exporter pod annotations are as follows:
prometheus.io/scrape:Set to true by default; if set to false, this annotation will exclude the pod from the scraping process.prometheus.io/path:/metrics, is the default settingprometheus.io/port:8080, is the default annotation
In an RBAC authentication environment like OpenShift, a ClusterRole and Role Binding must be created to allow Prometheus to scrape the Trilio metrics from the Trilio Metrics Exporter pod running in the Trilio installation namespace.
To expose the Trilio metrics to OpenShift's native Prometheus deployment, you need to create a Kubernetes Service for the k8s-triliovault-exporter, and in this example, the service should be a NodePort.
Create a Service Monitor to define the Trilio Exporter as a target to be monitored in Prometheus.
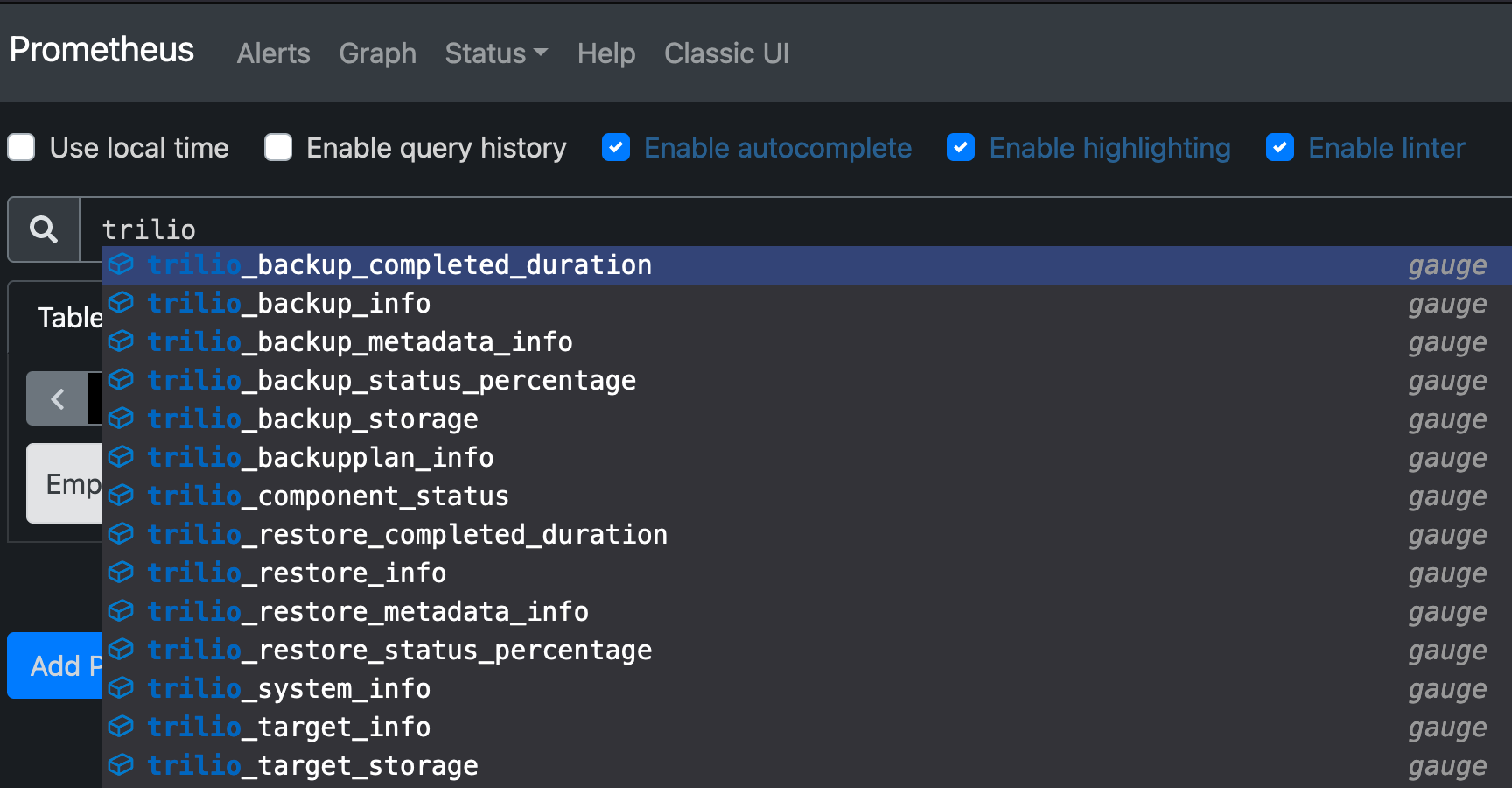
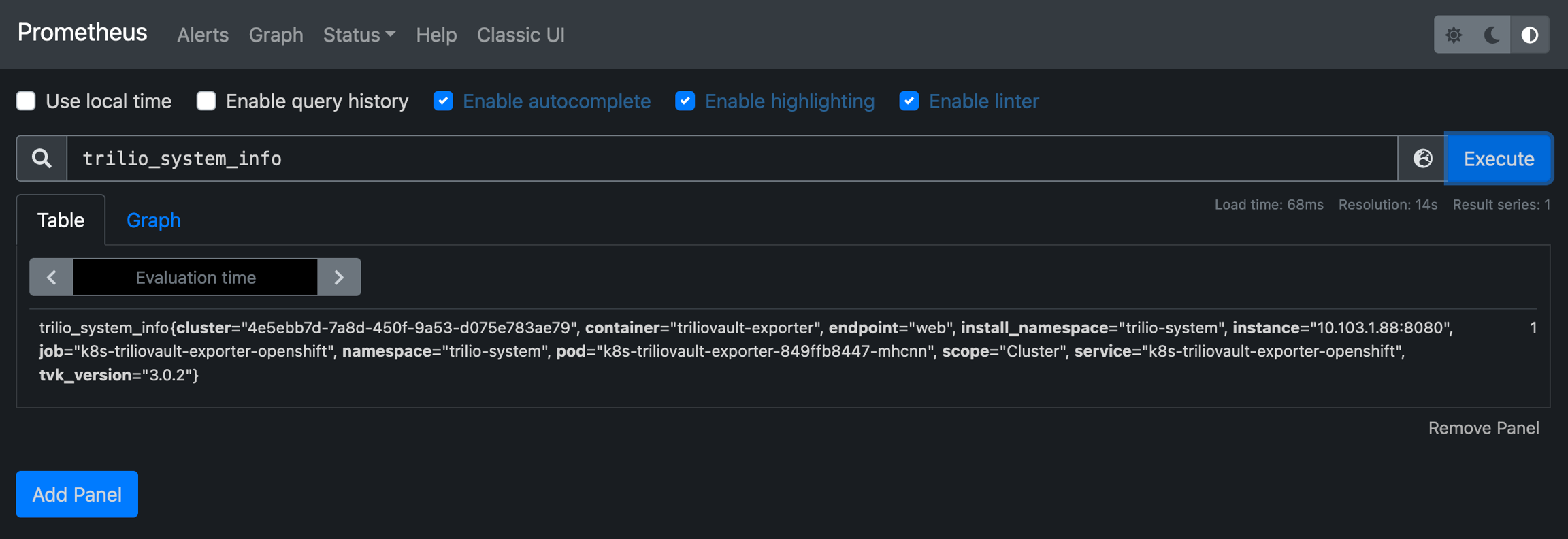
Select the metric trilio_system_info and click the "Execute" button. You should see the table beneath the query field populate with data if the Trilio Exporter is being scraped as expected.
About the Trilio Grafana Dashboards
Grafana Dashboards can be created with the Trilio metrics that you have pulled into your OpenShift native Prometheus deployment.
Trilio provides pre-created Grafana dashboards to make monitoring and observing your backups and restores convenient.
The Trilio Grafana dashboards provide detailed insight into the following aspects of Trilio's Backup and Restore operations:
Backups
Restores
Targets
BackupPlans
Using the Trilio Grafana Dashboards
The dashboards can be imported into a Grafana instance following instructions from the Grafana project page.
Learn more about the available Trilio Dashboards.
Make sure that you satisfy all dependencies for each dashboard.
The Trilio dashboards will not function correctly with unmet dependencies.

About Trilio Exported Metrics
Learn more about Trilio's Exported Prometheus Metrics and their associated tags and values.
Troubleshooting
Problems? Learn about Troubleshooting Trilio for Kubernetes