Uninstall
This section describes how to uninstall Trilio for Kubernetes (T4K)
There are two types of uninstallation of T4K:
Application uninstallation
Complete T4K cleanup
Application Uninstallation
Application uninstallation only deletes the T4K application and keeps all T4K custom resources. Users can follow these steps in case retaining the backups after application uninstallation is required. e.g. upgrade
RedHat OpenShift User Interface
Delete the Trilio Manager CR from Trilio for Kubernetes operator using OpenShift user interface console
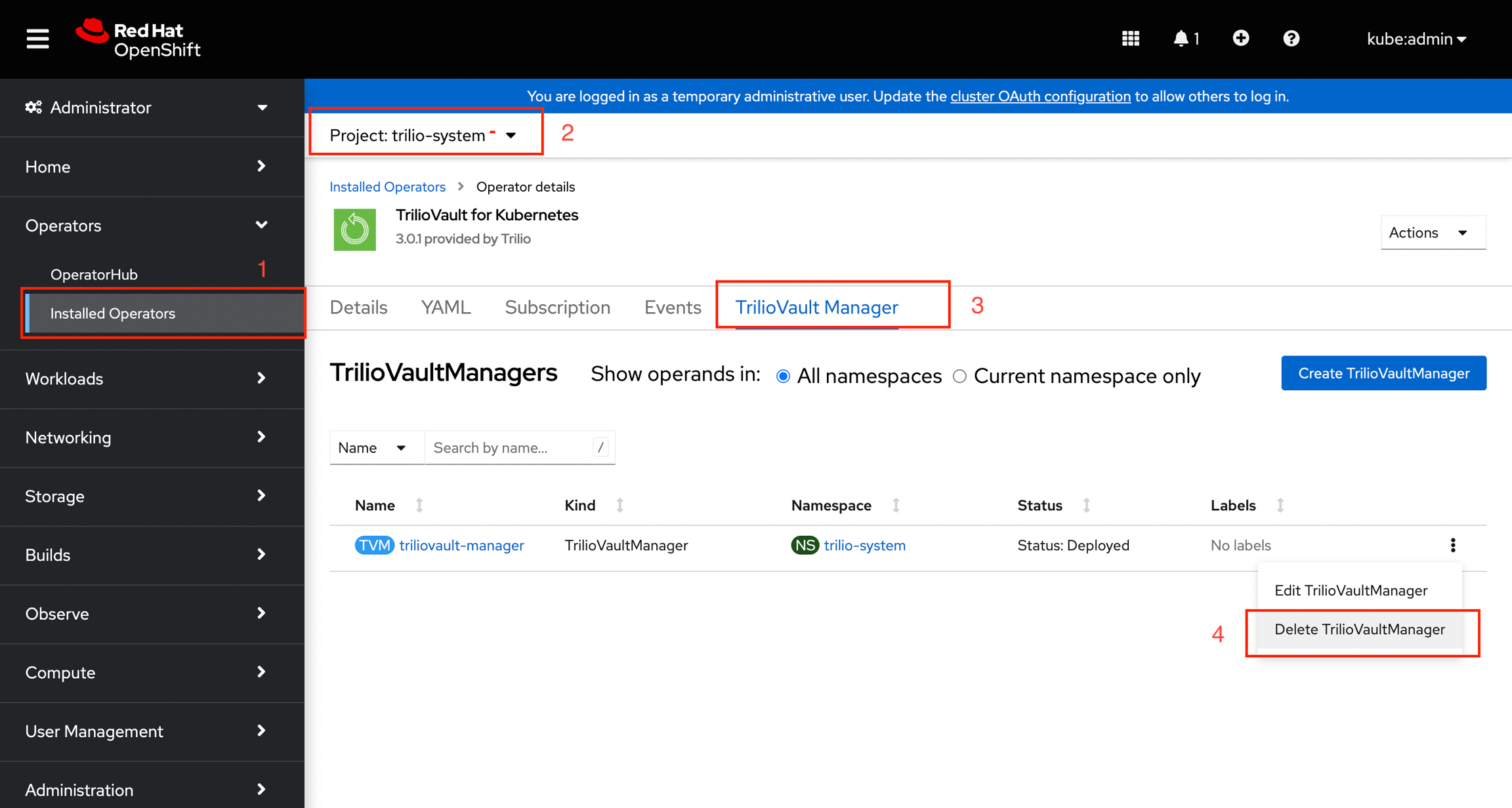
Uninstall the Trilio for Kubernetes Operator - can be done directly from the OpenShift user interface console. After a successful uninstall the Trilio application will not be available.
Upstream Kubernetes
Delete the Trilio Manager CR. When you uninstall the TVM CR, the
triliovault-managerhelm release will be uninstalled.
kubectl delete tvm triliovault-manager --namespace <T4K-installation-namespace>
If delete TVM CR triliovault-manager gets stuck then on another terminal, edit the TVM CR, remove the finalizer section and save it.
kubectl edit tvm triliovault-manager --namespace <T4K-installation-namespace>
Remove below section:
finalizers:
- uninstall-helm-release
This will complete the delete operation.
2. Uninstall the Helm Operator
helm uninstall triliovault-operator --namespace <T4K-installation-namespace>
Complete T4K Cleanup
Note: Complete cleanup of T4K will remove all of T4K's custom resources - backup, restore, target etc along with the application itself. If users wish to only remove application while keeping the backups as is, follow the application uninstallation guide mentioned above.
To cleanup Trilio for Kubernetes, the custom resources, CRDs and the Operator must be removed from the Kubernetes cluster or namespace. There are two ways users can cleanup T4K - automated (via a Trilio provided plugin) or manually removing all the items.
Automated Cleanup
Trilio provides a plugin that automates the uninstall of all the resources and objects created to support the solution. The automation provides a non-interactive mode to allow unattended uninstall of the solution, and also provides an interactive mode to specifically uninstall different components. For further details, refer to the T4K Cleanup Plugin.
Manual Cleanup
Users can manually cleanup components of the Trilio solution using the steps mentioned below
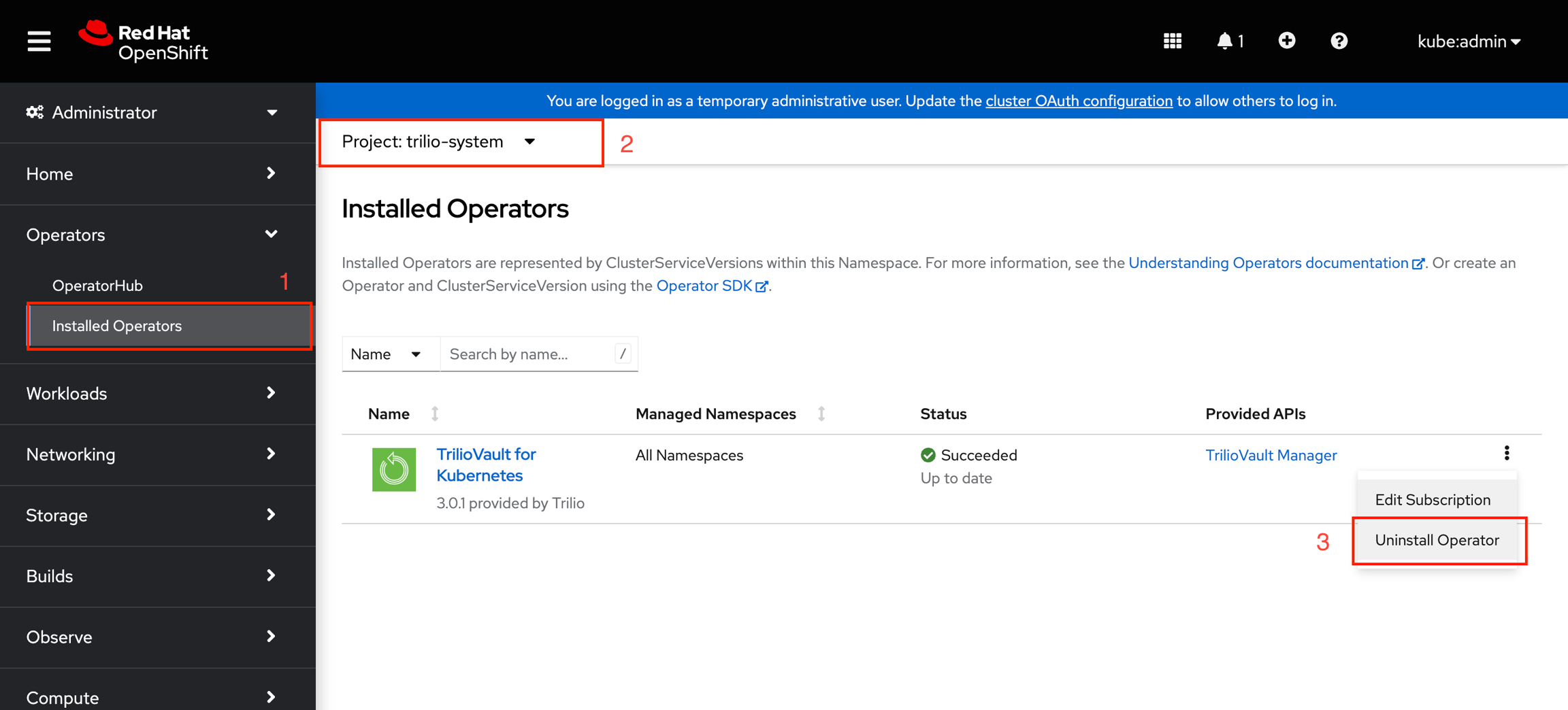
RedHat OpenShift User Interface
Delete all the custom resources associated with Trilio - Backup, Restores, Targets, Hooks, BackupPlans, ClusterBackupPlan etc.
Delete the Trilio Manager CR from Trilio for Kubernetes operator using OpenShift user interface console

Uninstall the Trilio for Kubernetes Operator - can be done directly from the OpenShift user interface console. After a successful uninstall the Trilio application will not be available.

Do not forget to delete the Trilio CRDs from the CRD page of OpenShift. Or run
oc delete crds $(oc get crds | grep trilio | awk '{print $1}')from OpenShift CLI
Upstream Kubernetes
Use the following steps to cleanup Trilio for Kubernetes on all other certified Kubernetes distributions where the Trilio operator was installed via Helm.
Delete all the custom resources associated with Trilio - Backup, Restores, Targets, Hooks, BackupPlans, ClusterBackupPlan etc.
Delete the Trilio Manager CR. When you uninstall the TVM CR, the
triliovault-managerhelm release will be uninstalled.
kubectl delete tvm triliovault-manager --namespace <T4K-installation-namespace>
If delete TVM CR triliovault-manager gets stuck then on another terminal, edit the TVM CR, remove the finalizer section and save it.
kubectl edit tvm triliovault-manager --namespace <T4K-installation-namespace>
Remove below section:
finalizers:
- uninstall-helm-release
This will complete the delete operation.
3. Uninstall the Helm Operator
helm uninstall triliovault-operator --namespace <T4K-installation-namespace>
4. Delete all the Trilio CRDs
kubectl delete crds $(kubectl get crds | grep trilio | awk '{print $1}')