Namespace & application scoped
Regardless of from where the Restore operation is initiated, the workflow for the operation is the same, ensuring consistency and simplicity.
For the restore workflow, there are four tabs presented to the user Basic Tab Resource Selector Transforms Hooks Configuration
Basic Tab
This tab cover general restore properties for the backups and snapshots such as name, namespace, secrets (if encrypted) and Restore flags
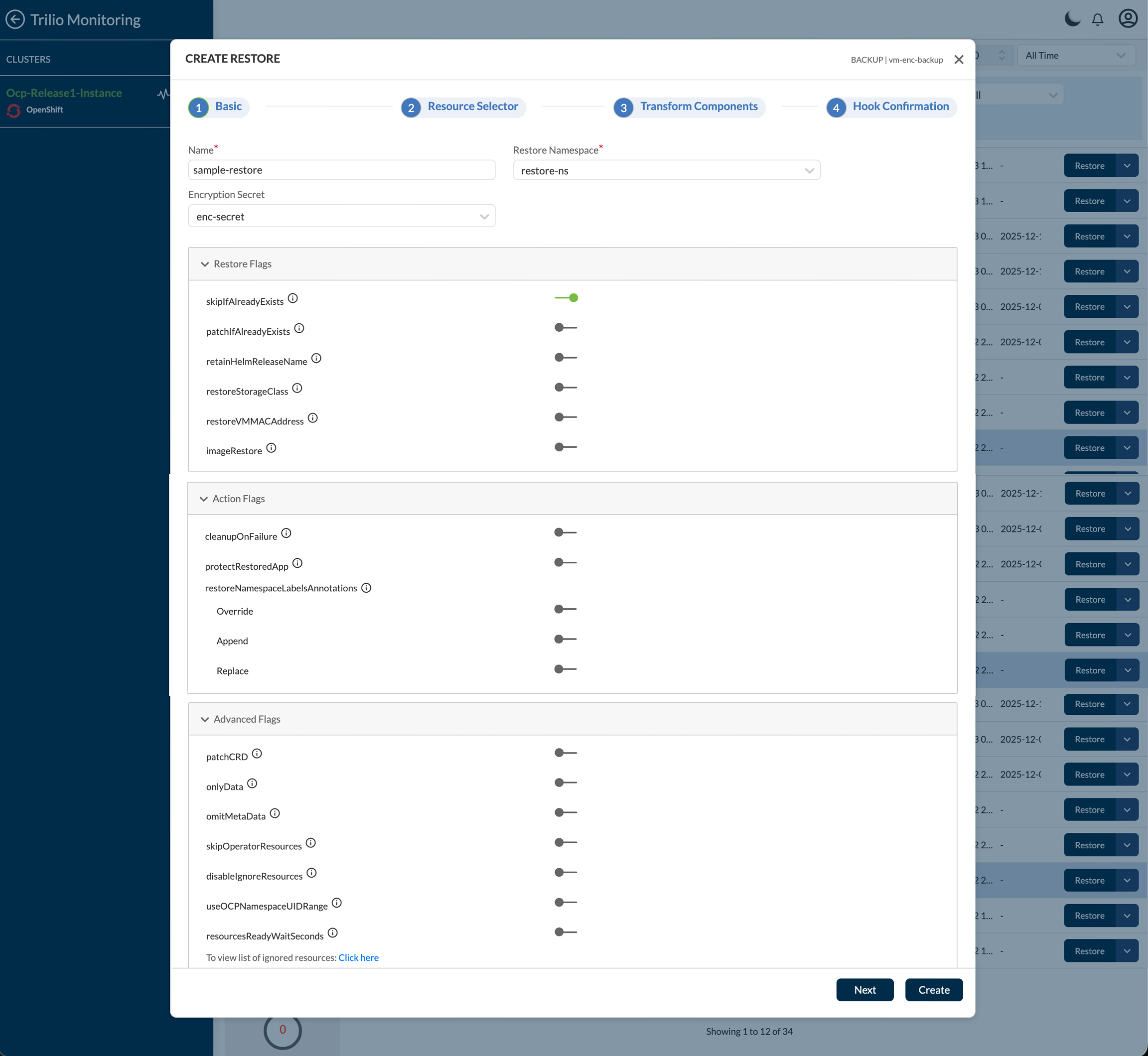
Name - Enter the meaningful name of Restore in this field.
Namespace - Select the Namespace in which user wants to take Restore of a Backup or a Snapshot. You can create a new Namespace from dropdown option "+ New Namespace"
Encryption Secret - Select the same secret which is selected in Backup plan from which Backup or Snapshot is created. You can create a new Secret from dropdown option "+ New Encryption Secret"
Restore Flags - As part of every restore, users can select different restore flags to define how the restore should happen. For detailed information about each flag, see the Restore Flags Guide
The following flags are provided:
Restore Flags
SkipIfAlreadyExists - Specifies whether to skip restoring resources if they are already found in the namespace in which the backup is being restored. This is only applicable for metadata resources and not data resources (PV/PVC). For more details with examples, refer SkipIfAlreadyExists
PatchIfAlreadyExists - Specifies whether to patch the spec section of an already existing resource found in the namespace at the time of restore. For more details with examples, refer PatchIfAlreadyExists.
RetainHelmReleaseName - Specifies if a user wants to retain the helm release name after restore. For more details with examples, refer RetainHelmReleaseName.
RestoreStorageClass - This flag specifies whether the storage class should be restored on site instance or not. For more details with examples, refer RestoreStorageClass.
RestoreVMMACAddress - Specifies whether to retain the original MAC address of the VM during restore instead of assigning a new one. For more details with examples, refer RestoreVMMACAddress.
ImageRestore Restores the container images from the backup. For more details with examples, refer ImageRestore.
Registry Registry to which the backup container images should be restored.
Repository Repository in which the restored images should be placed.
RegistryAuthSecret Authentication secret of type
kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjsonused to push the images to the restore registry.
Action Flags
CleanupOnFailure - Specifies whether to perform cleanup of resources created along with reverting updated resources in case the restore operation fails. For more details with examples, refer CleanupOnFailure.
ProtectRestoredApp - Specifies whether to create a backupplan at the destination namespace/cluster to protect the application after it has been restored. With this flag, users can ensure that their application is protected no matter which cluster it runs on. For more details with examples, refer ProtectRestoredApp.
RestoreNamespaceLabelsAnnotations Specifies the strategy for restoring labels and annotations of the backed-up namespace to the restored namespace.
Override Updates values of keys present in both the namespace and backup; adds missing keys from backup; does not remove keys that are not in the backup.
Append Keeps existing labels/annotations and only adds those not present from the backup.
Replace Removes all existing labels/annotations and replaces them entirely with those from the backup.
For detailed information about restoration strategies, configuration examples, and use cases, see Restore Namespace Labels and Annotations.
Advanced Flags
PatchCRD - Specifies whether to patch spec of an already existing CRD. For more details with examples, refer PatchCRD.
OnlyMetadata - Restores only the metadata components from a backup. For more details with examples, refer OnlyMetadata.
OnlyData - Restores only the data volume components from a backup. For more details with examples, refer OnlyData.
OmitMetadata - Specifies whether to omit metadata labels, annotations of resources while restoring them. For more details with examples, refer OmitMetadata.
SkipOperatorResources - Specifies whether to omit operator resources at the time of restore (for the use case when an Operator is already present, but the application of that operator needs to be restored). For more details with examples, refer SkipOperatorResources.
DisableIgnoreResources - Specifies the behaviour of the default list of resources being ignored at the time of restore. If set to true, those resources will not be ignored. For more details with examples, refer DisableIgnoreResources.
UseOCPNamespaceUIDRange - Openshift specific flag to restore the data with the ocp namespace UID range. For more details with examples, refer UseOCPNamespaceUIDRange.
ResourcesReadyWaitSeconds - This holds the wait time in seconds for which, TVK application will wait for user application's resources to come up in the restore process. For more details with examples, refer ResourcesReadyWaitSeconds.
To view list of ignored resources: Click here
Next button - Click on Next if user wants to setup advance configuration in Restore.
Create button - Click on this button to directly create Restore without any advance configuration like Resource selector, transformation and hooks.
Resource Selector
When redirects from Basic tab and if Target browsing of Backup or Snapshot namespace is disable, user see a toggle to enable the target browsing.
 click on that toggle to enable the target browsing to set up a resource selector.
click on that toggle to enable the target browsing to set up a resource selector.
Include resources - Restore will done with only selected resources in this field. This wont Restore all other resources available in Backup or Snapshot.
1. Labels set - This tab is used to select the Labels to include In the Restore.
 2. Resources - This tab is used to select the Resources to include In the Restore.
2. Resources - This tab is used to select the Resources to include In the Restore.
 \
\
Exclude resources - Restore will done without selected resources in this field. This Restore all other resources available in Backup or Snapshot. This also have Label set selector and Resources selector same as Include Resources.
Transforms
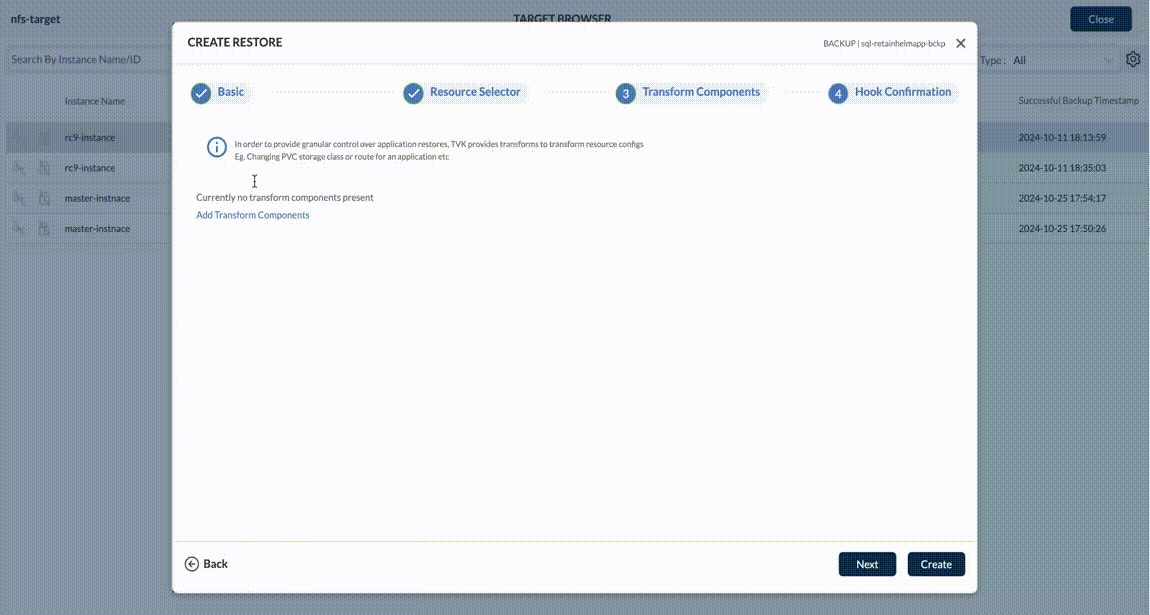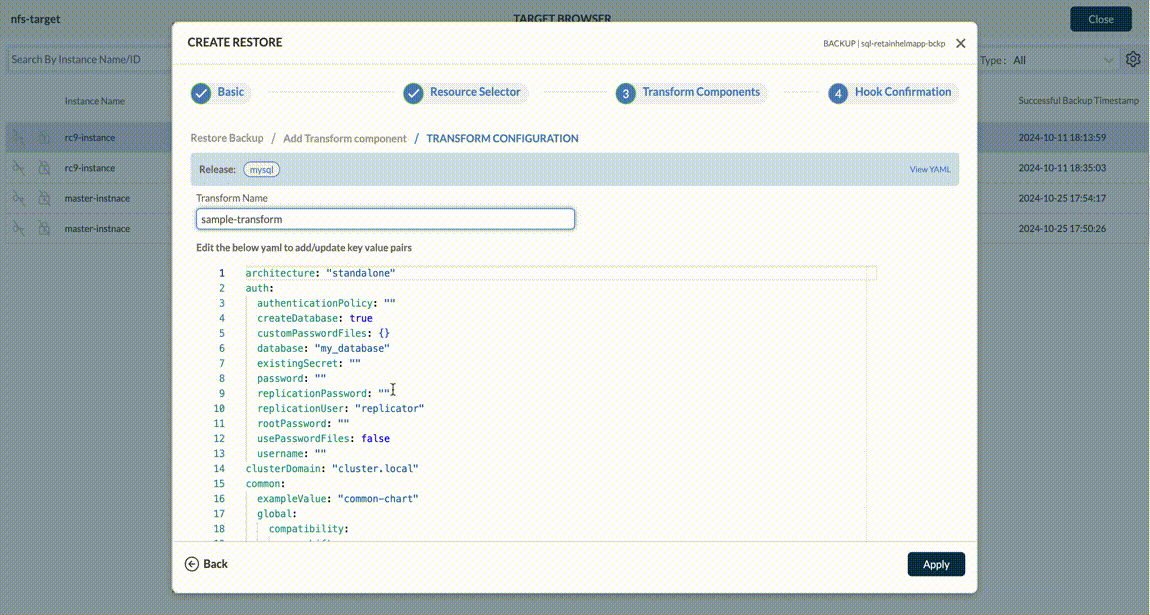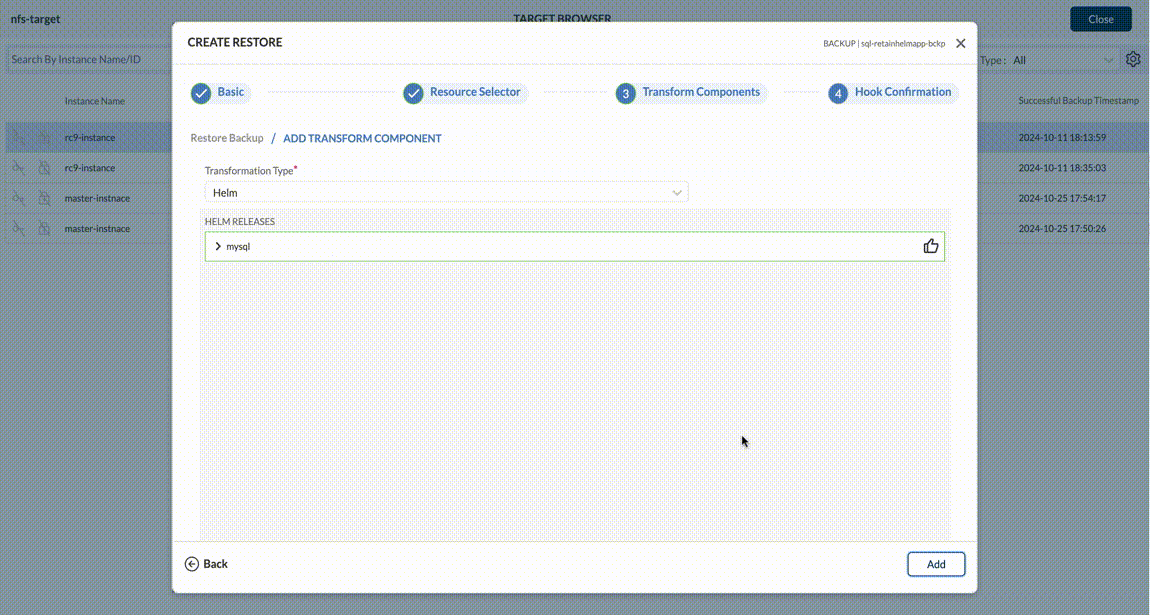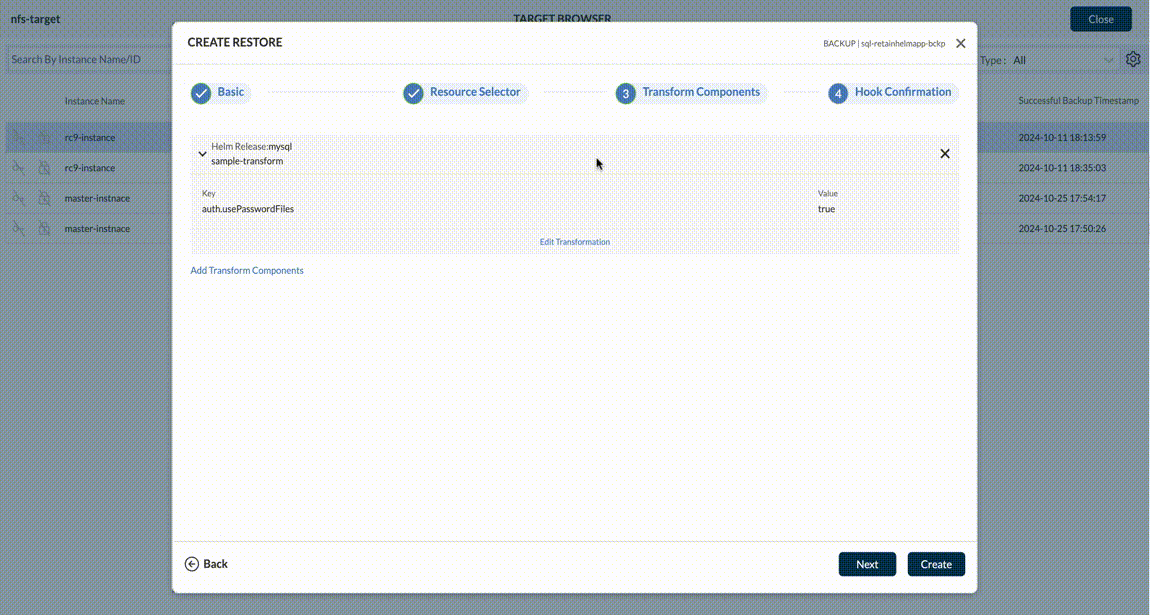
From a resource transform perspective, Trilio provides the ability to transform Helm Charts and transform custom resources. Helm charts can be transformed based on Key:Value pairs whereas custom resources can be transformed by specifying GVKO and Operation (Replace, Move etc.) type.
For both Helm and Custom Transforms - it fetches the metadata and populates it via dropdown menus and tables - to make it easy for the user to manage the granular details of the transforms. User can add custom transformation if Backup or Snapshots are of type operatorTransforms, custom, virtual machine like below.
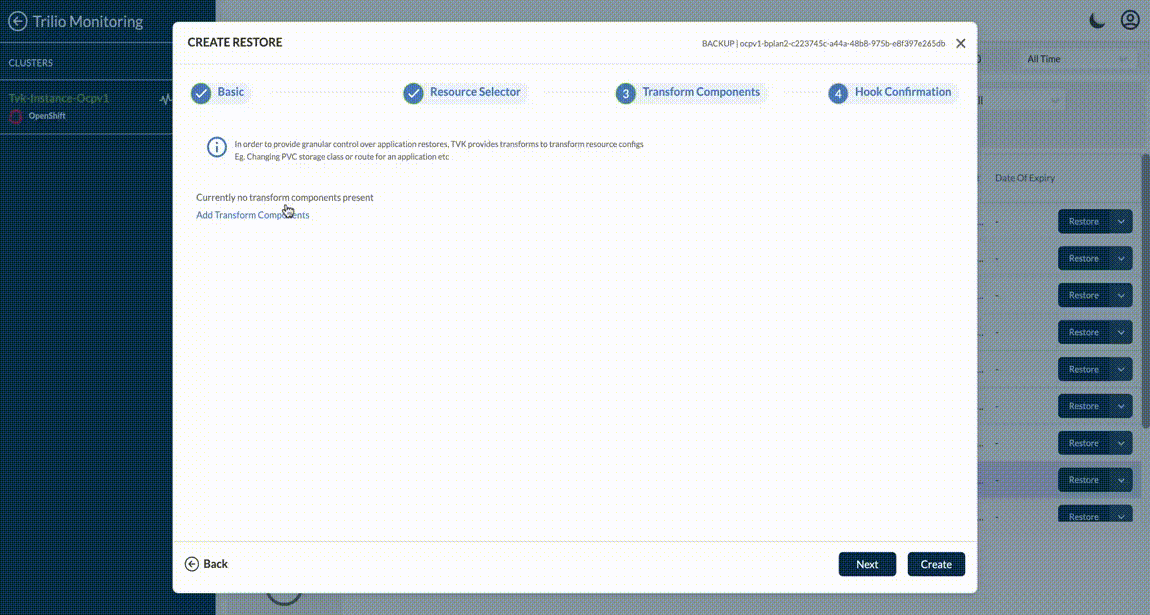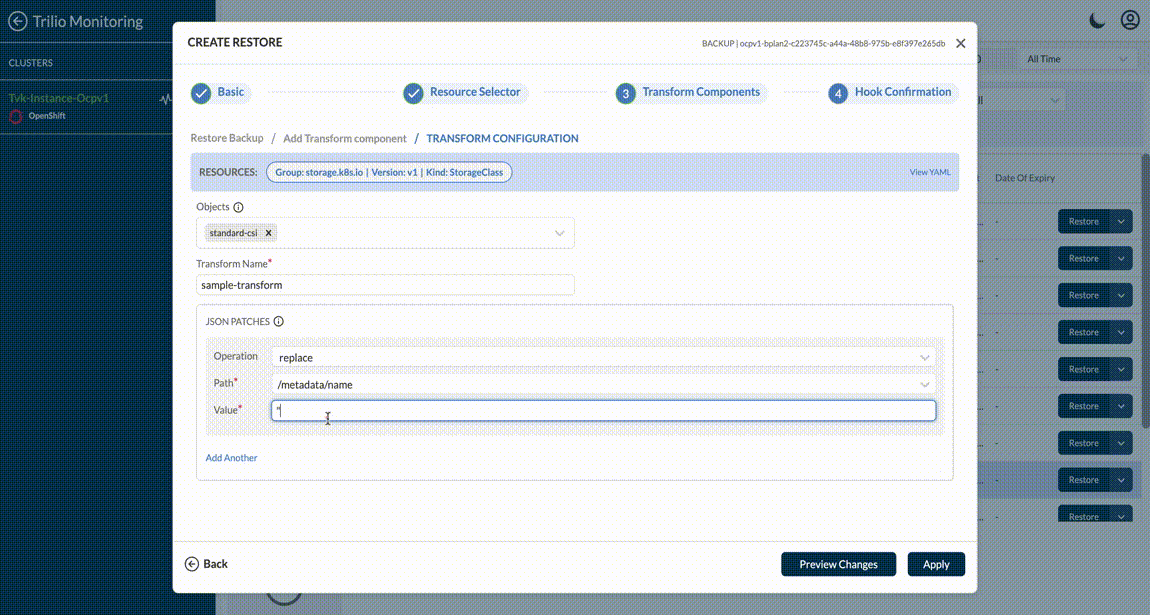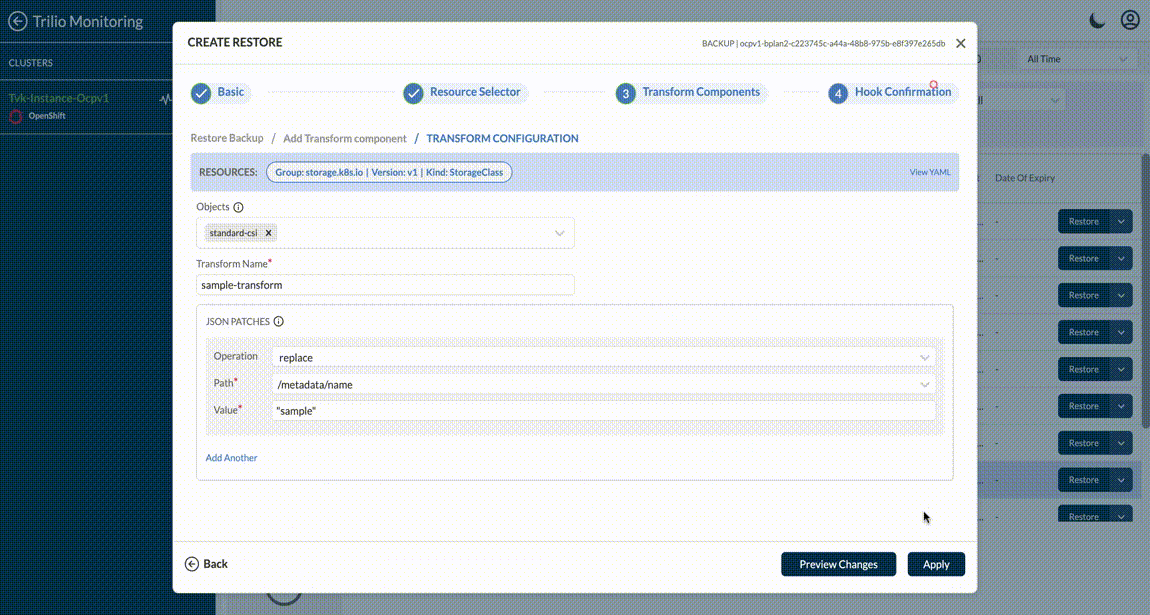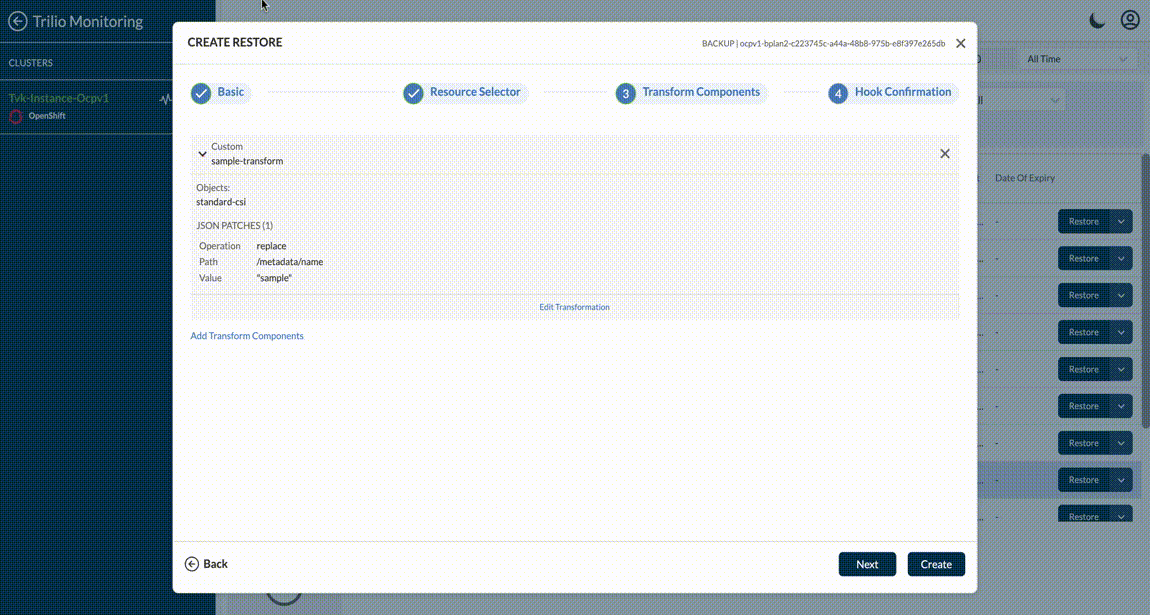
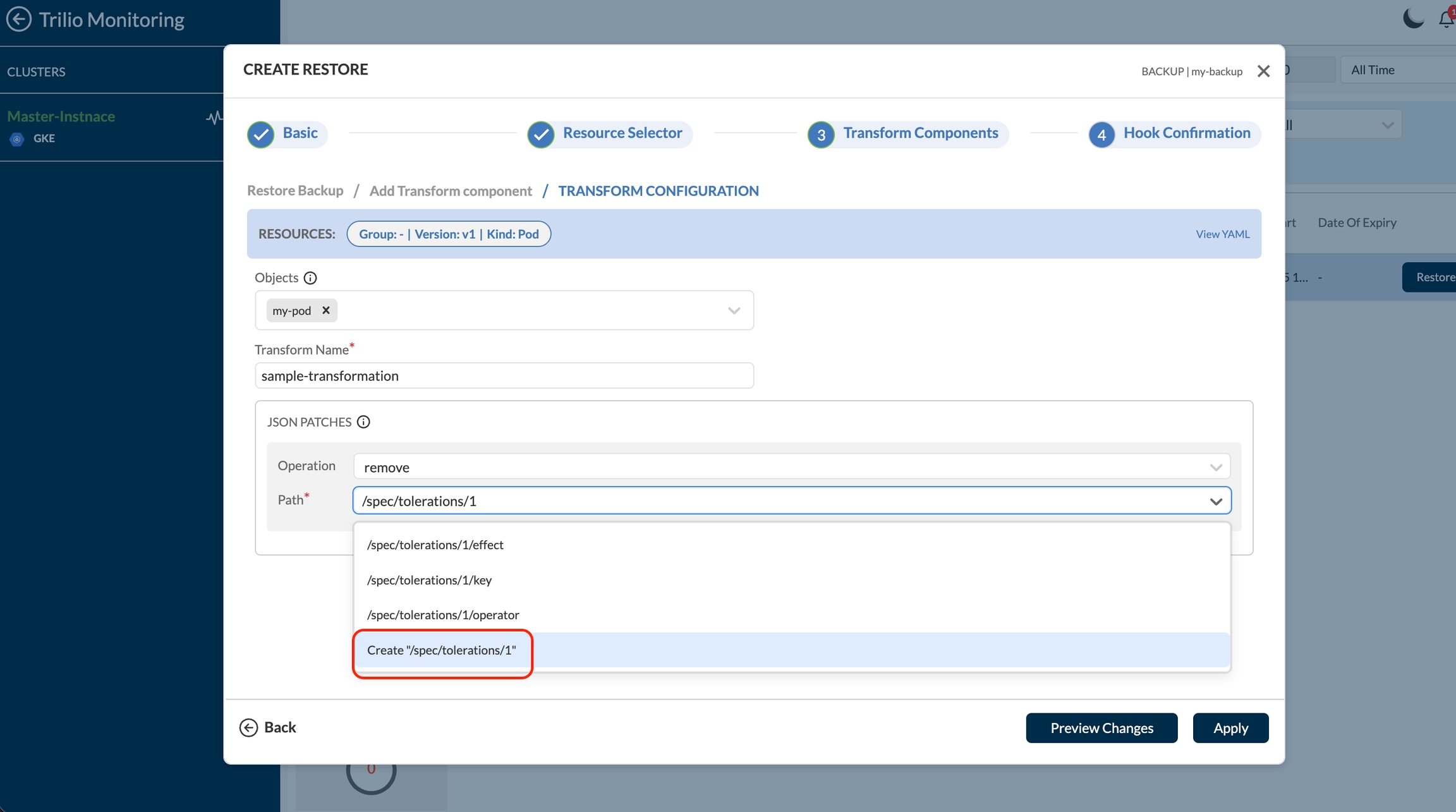
If the transformation path doesn’t appear in the list, you can manually create it by typing the path and selecting Create "<entered path>" from the dropdown. For example, if a user has the following section in any resource:
and the user wants to remove the second array item (effect: NoExecute), they can type the path and select the Create option. This will remove the entire second array item.
User can add helm transformation if Backup or Snapshots are of type helm type and if Backup or Snapshot is a Namespace scope, then retainHelmApp flag should enable in the Backup plan.
Hooks Configuration
TVK allows users to inject hooks similar to how they would apply hooks when performing a backup and snapshots. The restore Hooks are applied once the application is restored.
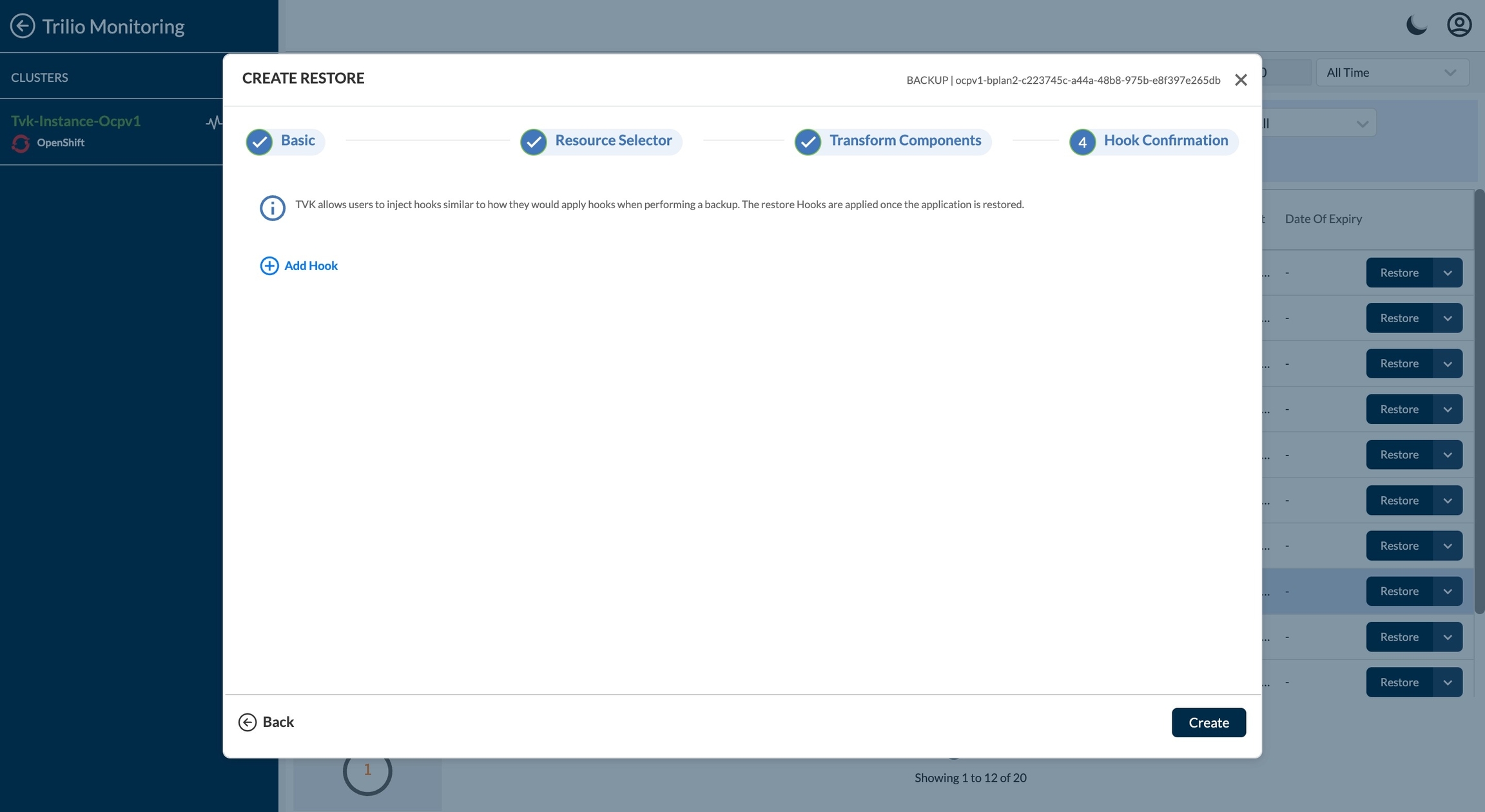
On click on the "+ Add hook" user can add the hook configuration.
When redirects from Basic tab and if Target browsing of Backup or Snapshot namespace is disable, user see a toggle to enable the target browsing.
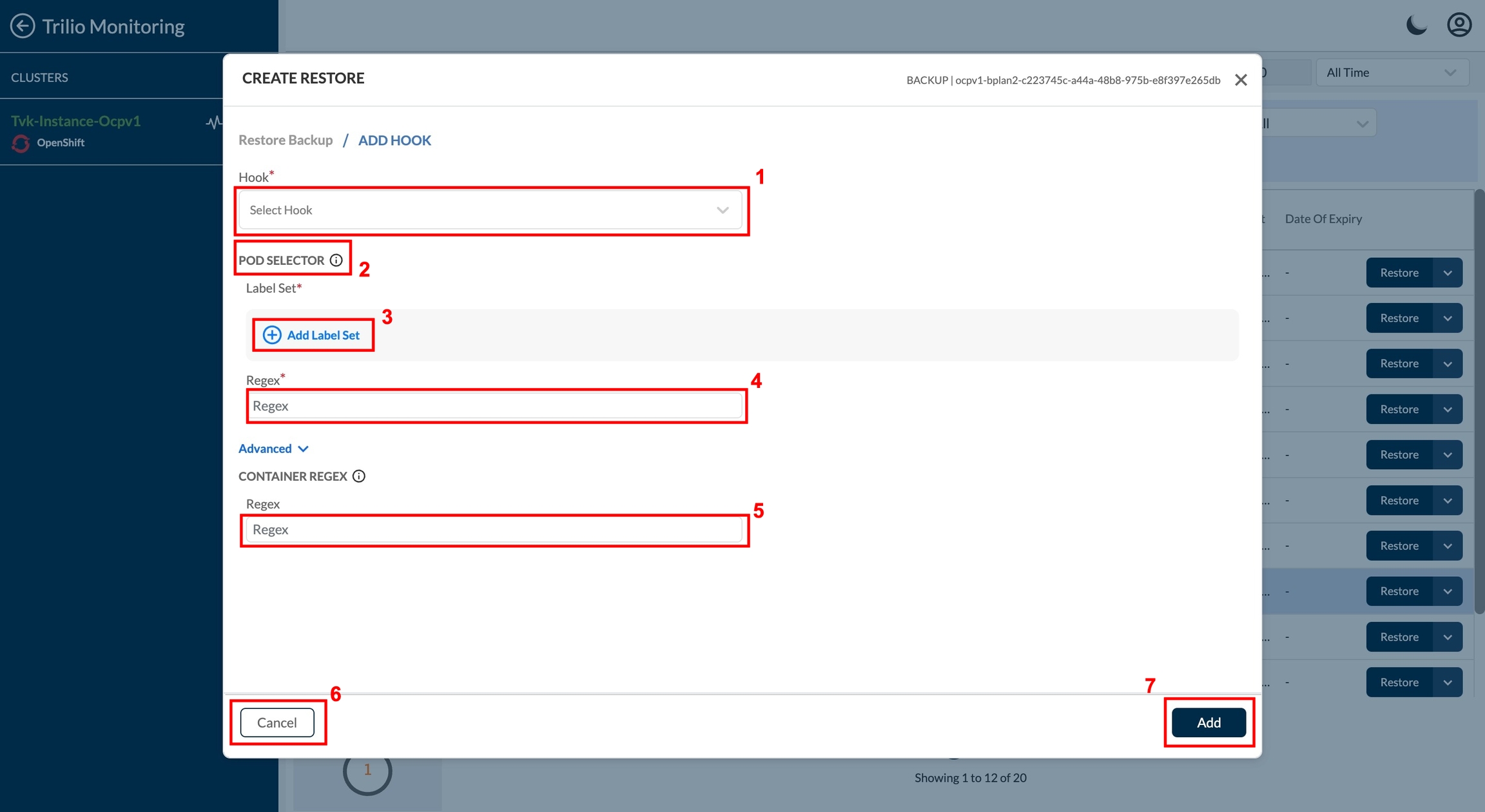
Hook - user can select existing hook from this listing. Also user can create a new hook by selecting "+ New Hook" option from dropdown value. For create new hook refer Create Hook. Here while creating hook, pre section is not a mandatory section as its not required in Restore process.
POD Selector - TVK provides the capability for selecting the pods to execute the hook commands. The pod selection can be done either by match labels/expressions or by matching a regex.
Note: Specifying either match label or a regex is mandatory
Scenario: User selects both match label and regex
System Behaviour: The system applies a 2 level filter first on the match labels and then on the regex
Scenario: If multiple pods are selected as part of the filtering, then which pods would the hook commands be executed on.
System Behaviour: The hooks commands will be executed on a) If a container regex is entered then it will run on the container within all the pods filtered. b) If no container regex is entered then it will run on all the containers within pods selected as a result of the filter.
Labels set - This tab is used to select the Labels to include In the Restore.
 \
\Regex - User can manually add the regex to execute inside the pod in this field.
Container Regex - TVK provides the capability for selecting the containers within the pods selected by the pod selector. The container selection can be done by matching a regex.
Cancel - Click on this if user wants to cancel this add hook configuration process.
Add - Click on this if user wants to add the hook configuration.