Immutable Backups
Learn about Trilio for Kubernetes Immutable Backups
Immutable backups are backups that can not be modified, altered or deleted by any user or process once they are created. Immutable backups are becoming increasingly popular as organizations strive to protect themselves against ransomware attacks, where hackers encrypt critical data and demand a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key. With immutable backups, organizations can be sure that their data is protected and can be restored without paying the ransom.
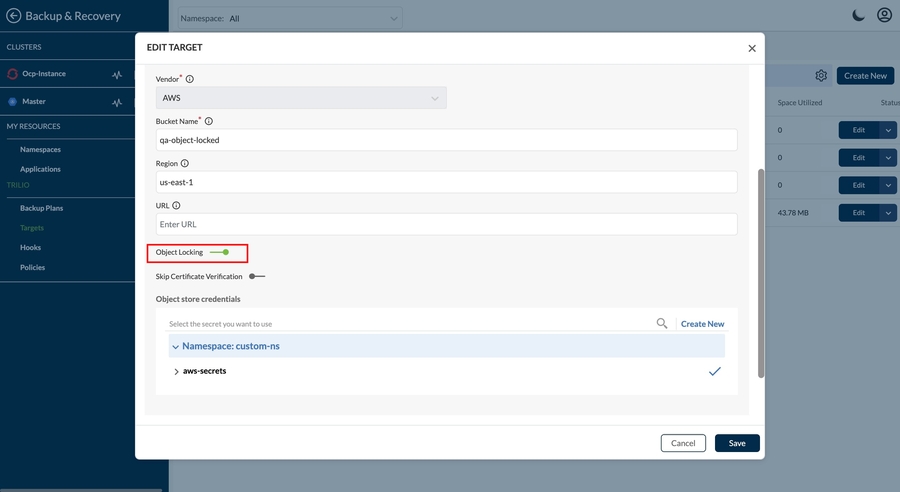
Trilio supports immutable backups on Object store targets which have object locking and versioning features enabled. For AWS S3 buckets, you can follow these steps to enable object locking. Trilio utilizes the underlying locking capabilities of the object store to create immutable backups which cannot be altered by users or the Trilio retention process.
The immutable backups can be taken on immutable targets and to denote such targets the user has to enable ObjectLockingEnabled field while creating the target.
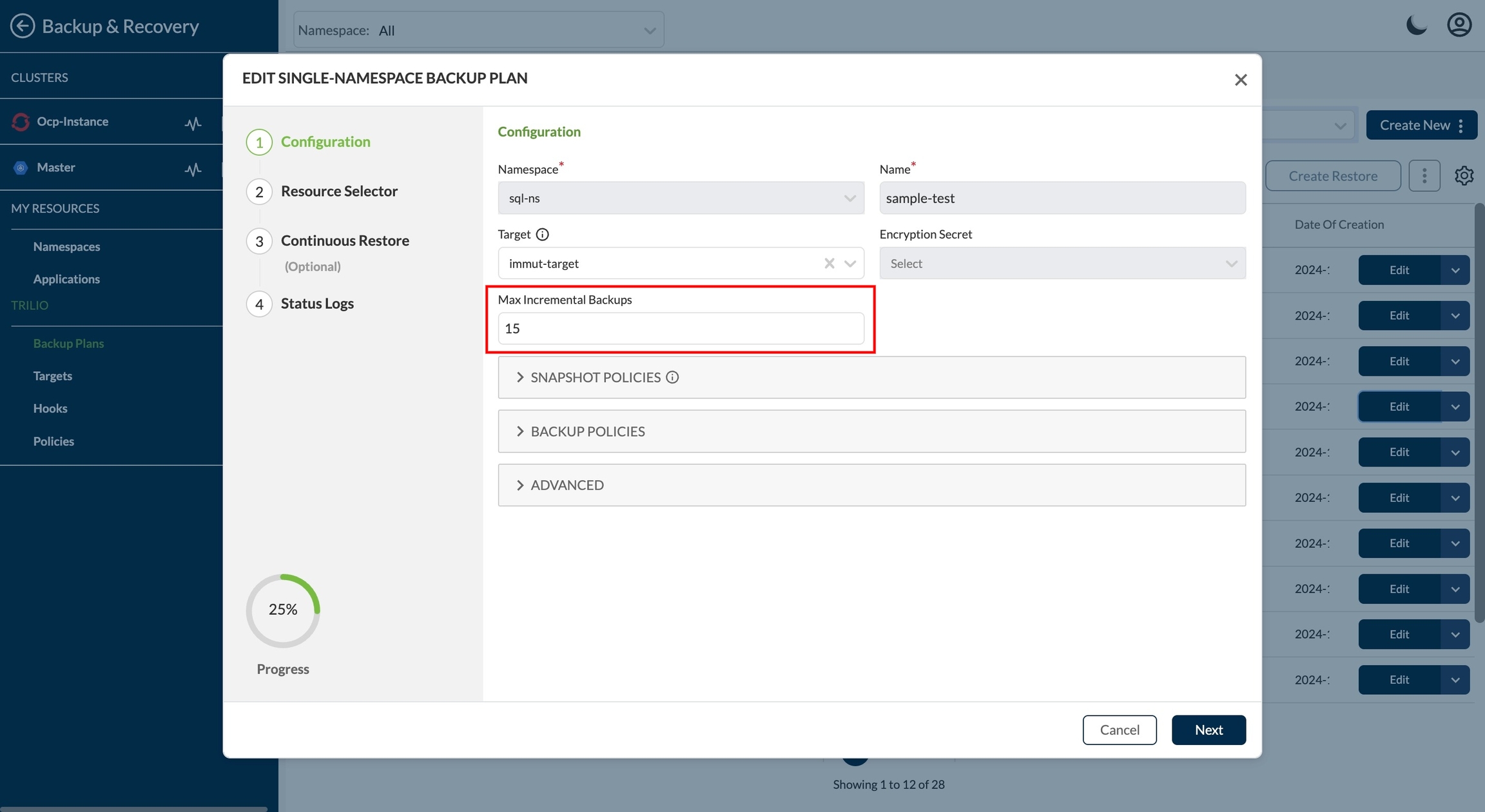
Immutable backups can not take "forever" incremental backups as we can with standard Trilio backups. Each immutable backup has a set number of incrementals to be taken, with the backup expiring at the conclusion of the last backup in the chain. Trilio has introduced a field MaxIncrBackupsPerFullBackup which represents the total number of incremental backups taken in the chain, after which a new full backup is created so that we can slowly retire the old backups we have written on the immutable target storage.
Based on the retention and schedule policy, Trilio will set the RetainUntilDate on the backup created on the target using the put-object-retention api call. These backups will be retained on the target until the RetainUntilDate has elapsed, after that those backups will be deleted. In case of incremental backups, the expiry date of first full backup and all subsequent incremental backups would be the expiry of last incremental backup. Schedule and Retention policies must be provided in an immutable backup as we need to calculate the probable expiry date.
 Trilio for Kubernetes will not delete backups/ snapshots from the target, they will be deleted automatically as per the retention policy of the S3 bucket, configured by the user.
Trilio for Kubernetes will not delete backups/ snapshots from the target, they will be deleted automatically as per the retention policy of the S3 bucket, configured by the user.